Figure 7.
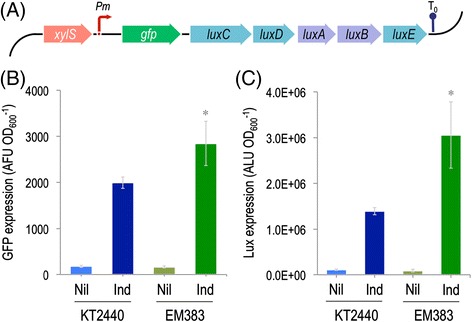
Evaluation of P . putida EM383 as a chassis for the heterologous expression of gfp and luxCDABE . (A) Schematic representation of the bi-cistronic GFP-LuxCDABE reporter in which both gfp (GFP: green fluorescent protein) and luxCDABE (LuxC: fatty acid reductase, LuxD: acyl transferase, LuxE: acyl-protein synthase, LuxAB: luciferase) from Photorhabdus luminescens are placed under the control of the inducible Pm promoter. The activity of Pm is controlled by the transcriptional regulator XylS. The transcriptional terminator included in the plasmid backbone is depicted as T0. The elements in this outline, borne by plasmid pGL-XP, are not drawn to scale. The reporter plasmid pGL-XP was used to establish a comparison of the expression levels of gfp (B) and luxCDABE (C) in wild-type KT2440 and in the streamlined EM383 strain in response to 3-methylbenzoate. Overnight cultures in rich LB medium were diluted to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.1, cells were further grown for 2 h, and then induced with 1 mM 3-methylbenzoate for 24 h. The reporter expression level was calculated by dividing either the arbitrary fluorescence units (AFU) or the arbitrary luminescence units (ALU) by the OD600. The bars represent the media and SD of three measurements from biological triplicates. Nil, no inducer; Ind, induced. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference for strain EM383 as compared to wild-type KT2440 according to the Student’s t test (P <0.05).
