FIGURE 4:
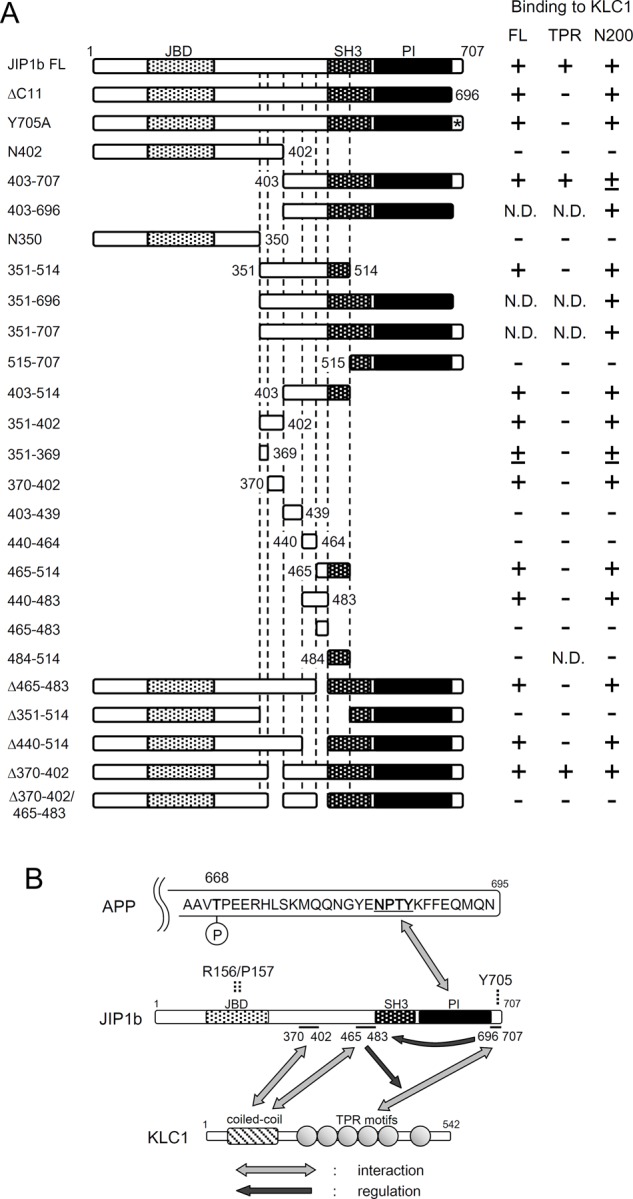
Summary of binding between JIP1b and KLC1, and schematic interactions between APP, JIP1b, and KLC. (A) Structures of JIP1b used in this study. Numbers represent amino acid positions. The asterisk indicates the position of alanine substitution for tyrosine (Y705A). Summary of JIP1b interactions with KLC1 (FL), KLC1 TPR domains (TPR), and the KLC1 N200 region (N200) is shown on the right, classified as binding (+), weak binding (±), and nonbinding (–). N.D., not determined. (B) Schematic interaction between the APP cytoplasmic region, JIP1b, and KLC. The NPTY motif of APP binds to the PI/PTB domain of JIP1b. Thr-668 in APP (numbering for APP695 isoform) is subject to phosphorylation. The 11 C-terminal amino acids of JIP (697YTCPTEDIYLE707), including Tyr-705, interact with the C-terminal half of KLC1, including the TPR motifs. The JIP1b370-402 and JIP1b465-483 regions were identified as novel binding sites for the N-terminal half of KLC1, including the coiled-coil/heptad repeats. The JIP1b465-483 region also showed regulatory activity in the interaction between the 11 C-terminal amino acids of JIP1b and the C-terminal half of KLC1. The C11-terminal region of JIP1b may be involved in the interaction between JIP1b465-483 and the N-terminal half of KLC1.
