Abstract
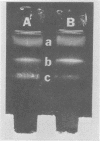
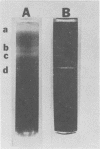
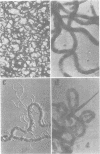
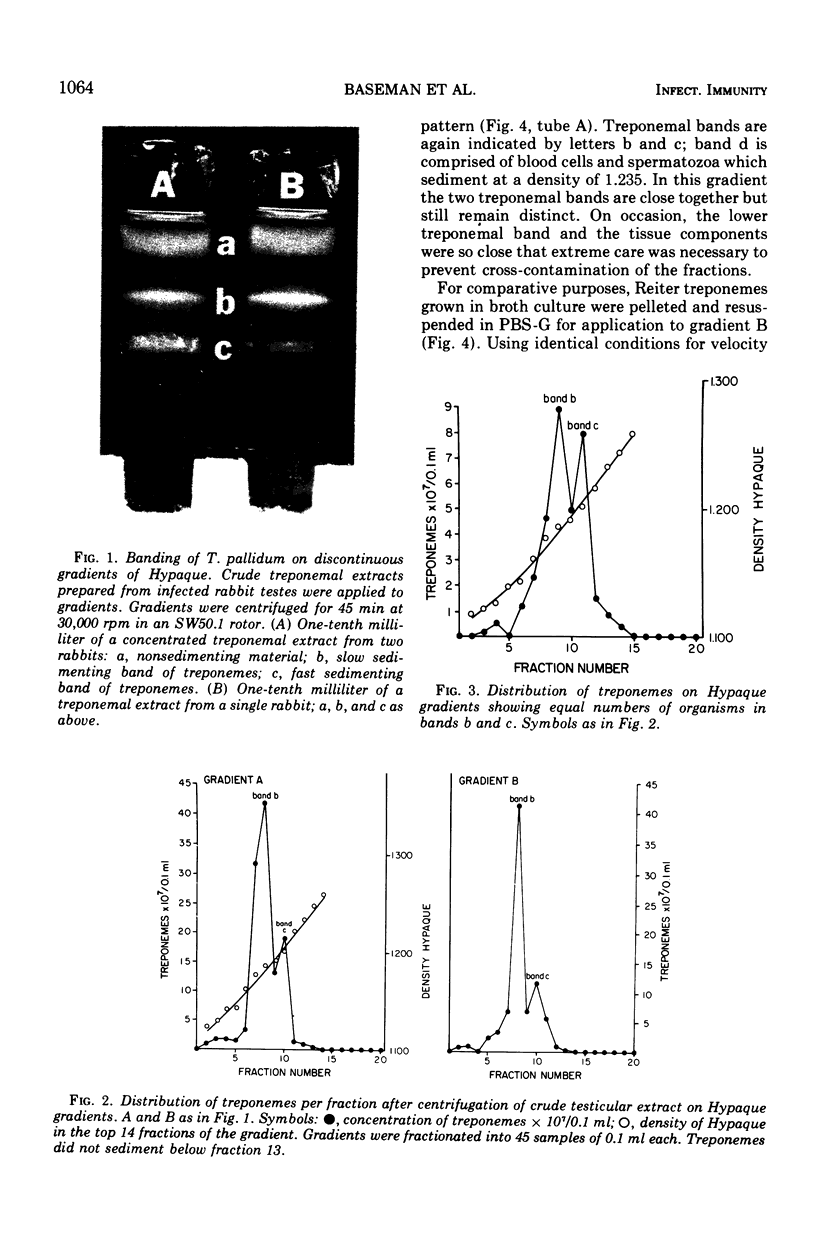
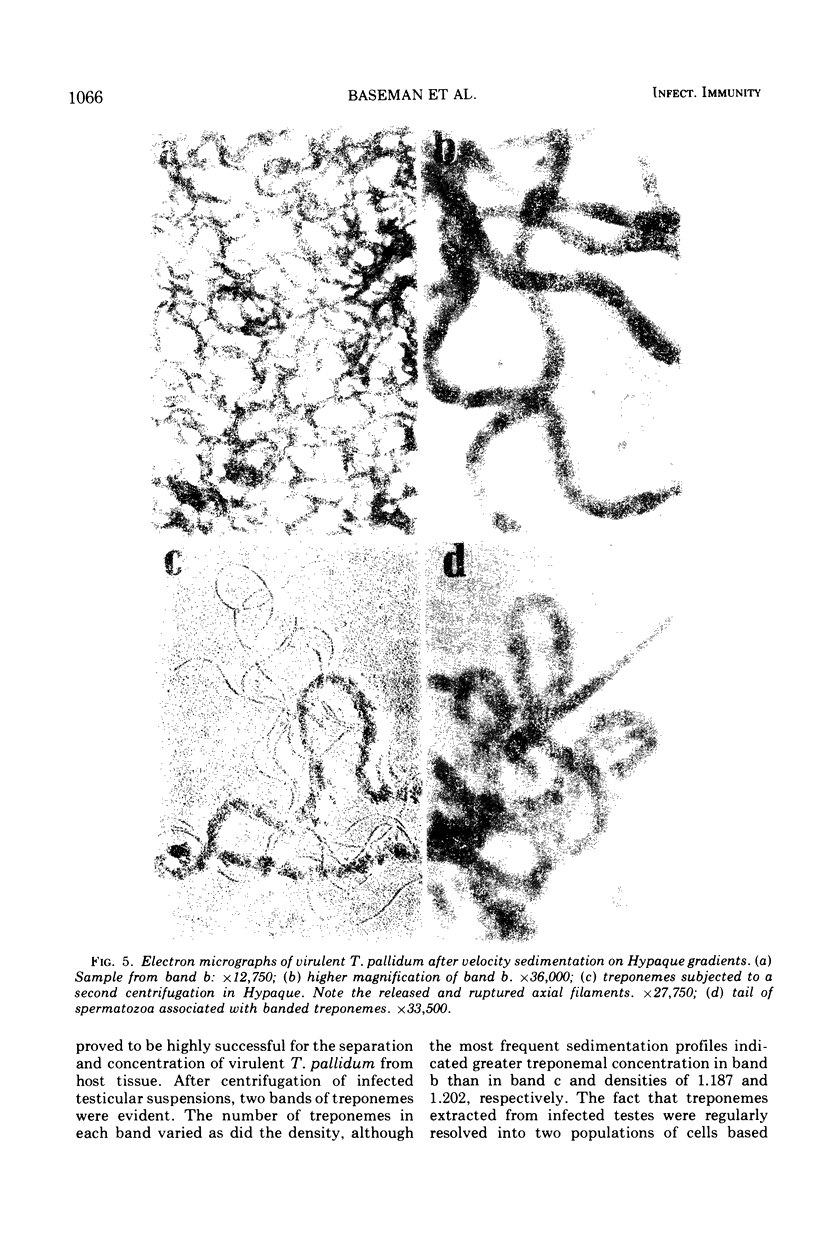
Virulent Treponema pallidum organisms, extracted from infected rabbit testes, were subjected to velocity sedimentation in discontinuous gradients of Hypaque, a high density, low viscosity material. After centrifugation of extracts at 20 C for 45 min at 100,000 x g, treponemes separated into two distinct bands based upon their relative velocities, although some variation was observed in the densities of the two bands and the number of treponemes per band. Rabbit tissue components sedimented more rapidly. Dark field and electron microscopy of preparations after velocity sedimentation indicated that treponemes retained general structural characteristics and no tissue contamination occurred in the treponemal fractions. Purification of treponemes in Hypaque resulted in their loss of motility and infectivity based upon animal inoculation. Antigenicity with respect to reactivity with antibody was preserved as shown by the high fluorescence intensity of treponemes in the fluorescent treponemal antibody adsorption test.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandler F. W., Jr, Clark J. W., Jr Passage of Treponema pallidium through membrane filters of various pore sizes. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Feb;19(2):326–328. doi: 10.1128/am.19.2.326-328.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden C., Nester E. W. Purification of competent cells in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):876–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.876-885.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauderdale V., Goldman J. N. Serial ultrathin sectioning demonstrating the intracellularity of T. Pallidum. An electron microscopic study. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Apr;48(2):87–96. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATHLEV T., PFAU C. J. PURIFICATION OF THE PATHOGENIC TREPONEMA PALLIDUM BY DENSITY GRADIENT CENTRIFUGATION. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17:130–134. doi: 10.1080/00365516509077298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Intracellular location of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in the rabbit testis. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):307–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.307-314.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamir H., Gilvarg C. Density gradient centrifugation for the separation of sporulating forms of bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 10;241(5):1085–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. L., Clark J. W., Jr, Cline G. B., Anderson N. G., Russell H. Separation of Treponema pallidum from tissue substances by continuous-flow zonal centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):714–720. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.714-720.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]