Abstract
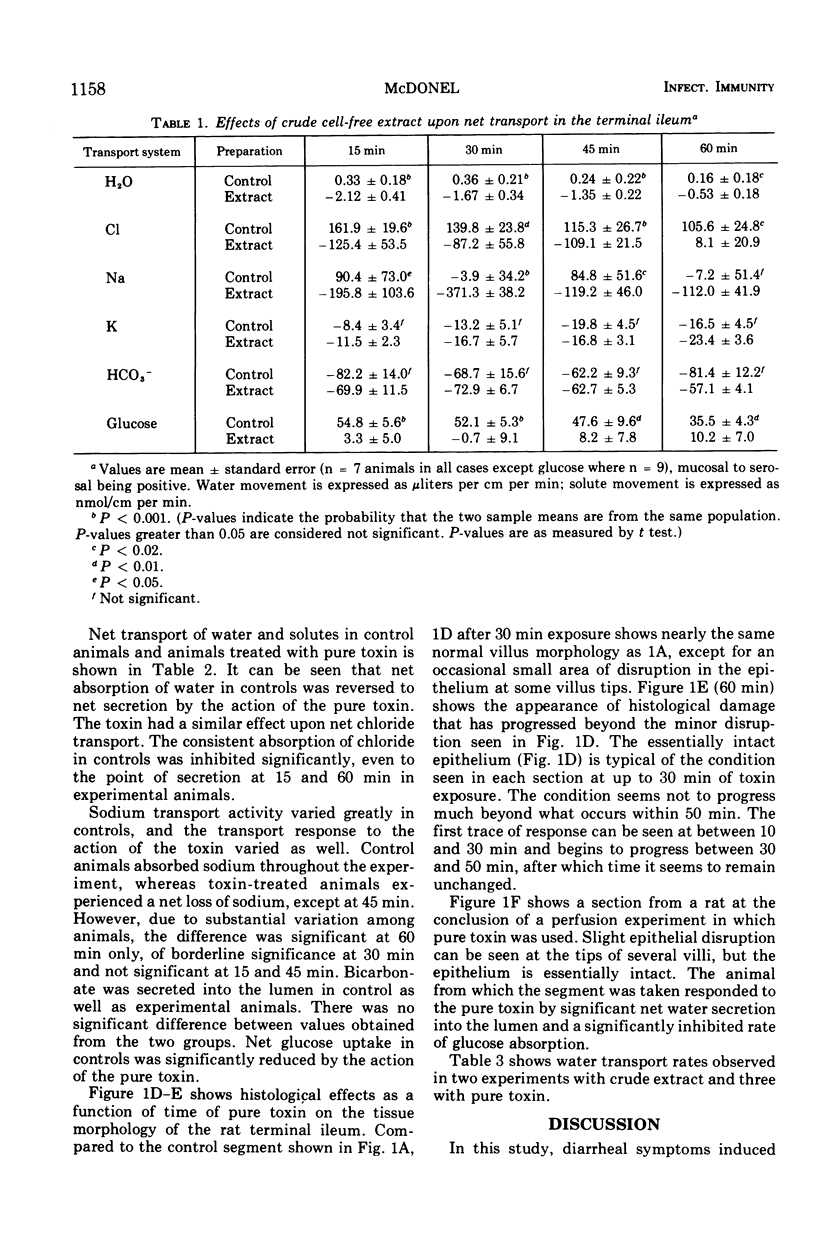
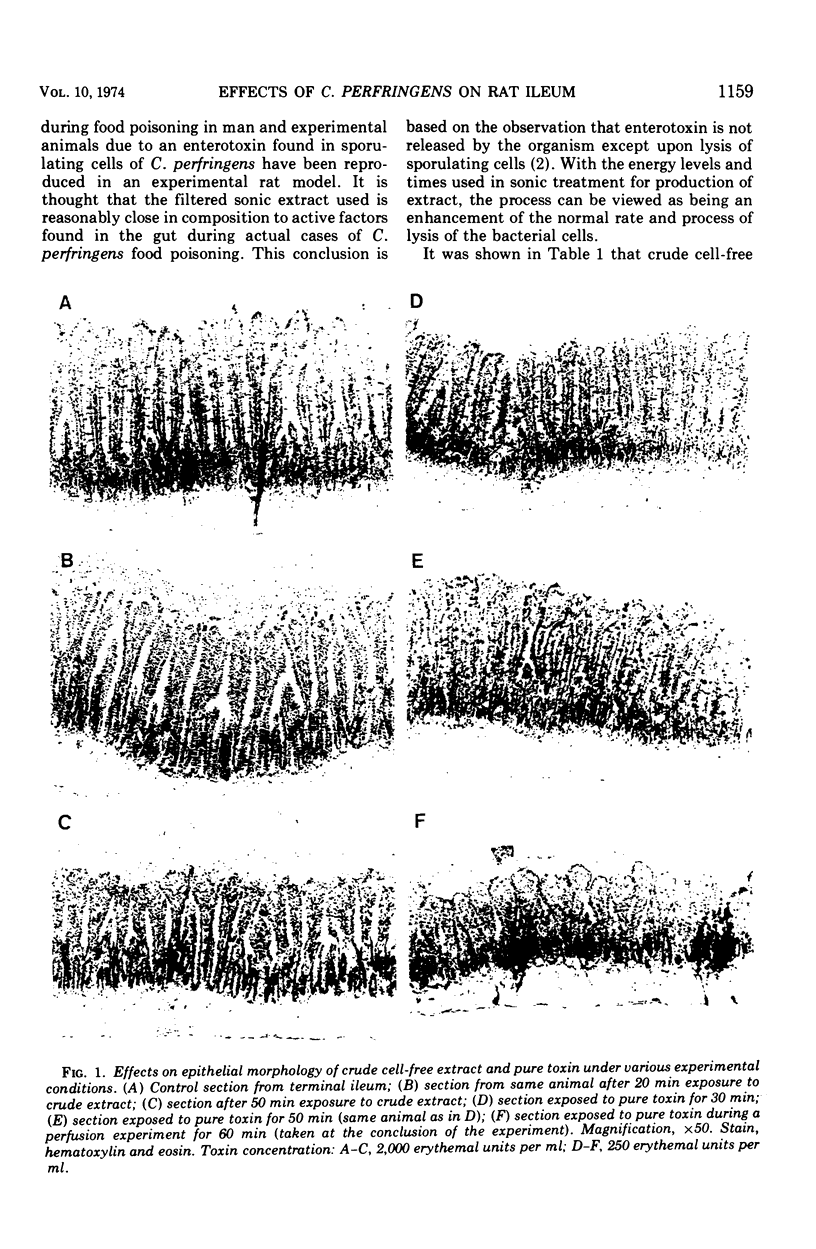
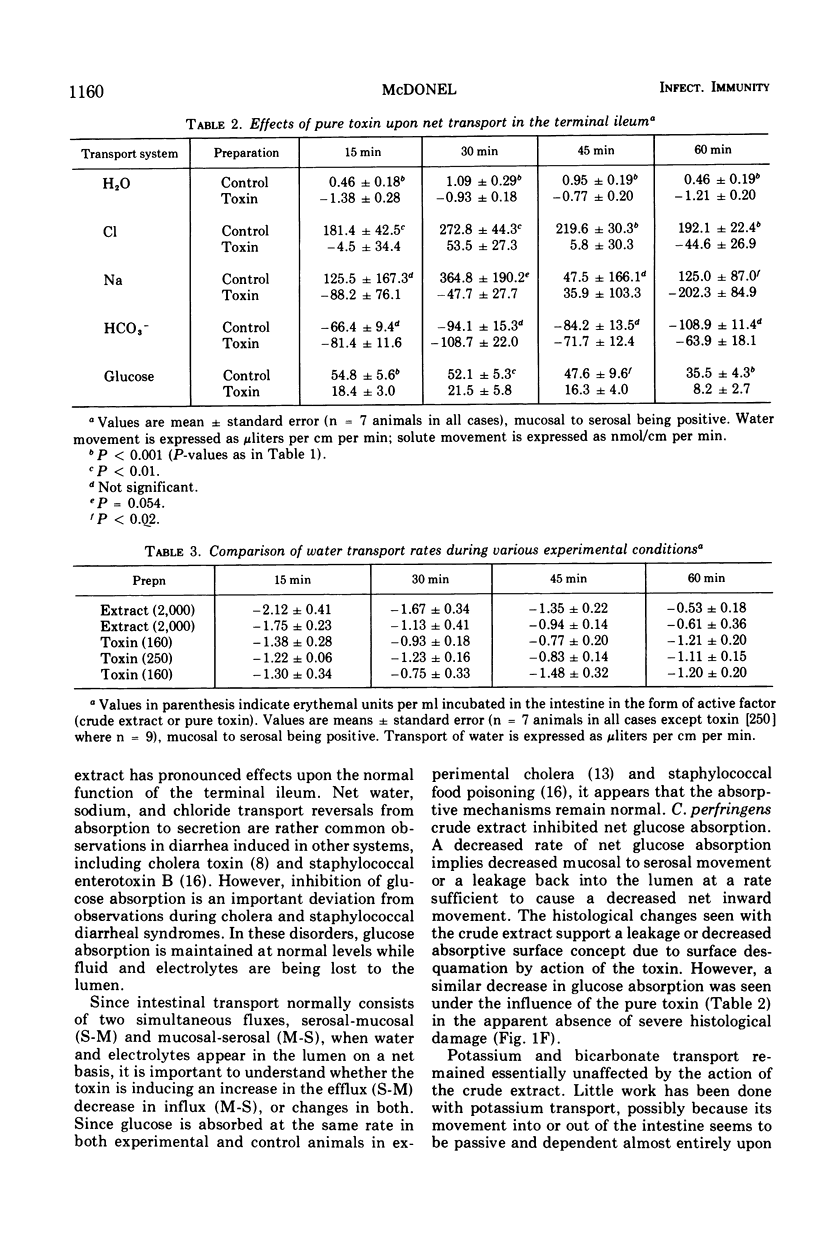
An experimental model was established using the terminal ileum of the rat for characterizing and studying the effects of crude cell-free extract from Clostridium perfringens upon physiological and histological parameters involved in the transport process. Further work was done with the model system using purified enterotoxin (protein) from the cell extract. Using an in vivo perfusion technique it was found that crude extract induces a reversal of net transport, from absorption in controls to secretion, of water, sodium, and chloride. Glucose absorption was greatly inhibited, whereas potassium and bicarbonate transports were unaffected. Crude extract also caused histological damage to the villus epithelium by denuding the villus tips, thereby leaving the lamina propria exposed. Similar responses in transport of water, sodium, chloride, bicarbonate, and glucose were caused by purified toxin. Little or no histological damage resulted from the pure toxin activity. However, the toxin was shown to have the capacity to denude villus tips under the proper experimental conditions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Experimental production of diarrhea in rabbits with Clostridium perfringens. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):765–770. doi: 10.1139/m69-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Ileal loop fluid accumulation and production of diarrhea in rabbits by cell-free products of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):86–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.86-94.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L. Time of enterotoxin formation and release during sporulation of Clostridium perfringens type A. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):932–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.932-936.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Niilo L., Dorward W. J. The role of enterotoxin in Clostridium perfringens type A enteritis. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jul;17(7):987–991. doi: 10.1139/m71-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A. Bicarbonate secretion in rat ileum and its dependence on intraluminal chloride. Am J Physiol. 1967 Dec;213(6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.6.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A. Effect of luminal chloride concentration on bicarbonate secretion in rat ileum. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):40–45. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Takeuchi A., Gangarosa E. J., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P. Pathogenesis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) dysentery. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):261–270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maenza R. M., Powell D. W., Plotkin G. R., Formal S. B., Jervis H. R., Sprinz H. Experimental diarrhea: salmonella enterocolitis inthe rat. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):475–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Schedl H. P. Total recovery studies of nonabsorbable indicators in the rat small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jan;58(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Plotkin G. R., Maenza R. M., Solberg L. I., Catlin D. H., Formal S. B. Experimental diarrhea. I. Intestinal water and electrolyte transport in rat salmonella enterocolitis. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):1053–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serebro H. A., Bayless T. M., Hendrix T. R., Iber F. L., McGonagle T. Absorption of d-glucose by the rabbit jejunum during cholera toxin-induced diarrhoea. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1272–1273. doi: 10.1038/2171272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Biological characteristics of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):89–96. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.89-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Purification and biochemical properties of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):662–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.662-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Asano T. Effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin B on intestinal transport in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):1793–1797. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]