FIGURE 7:
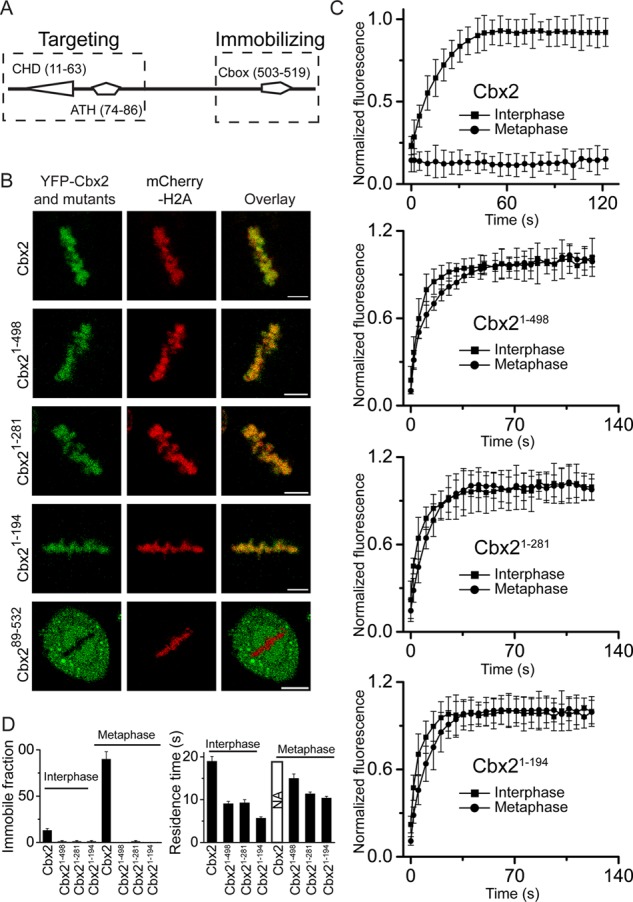
Analysis of structural elements of YFP-Cbx2 fusion protein required for its targeting and immobilizing. (A) Diagram of structural domains of Cbx2. The dashed rectangles indicate the region required for targeting Cbx2 to mitotic chromosomes (left) and the region required for immobilizing Cbx2 at mitotic chromosomes (right). ATH, AT-hook domain; Cbox, chromobox domain; CHD, chromodomain domain. The numbers in parentheses indicate the starting and ending of amino acid sequence. (B) Confocal images of YFP-Cbx2 and its variant fusion proteins in metaphase of HeLa cells. YFP-Cbx2 mutant and mCherry-H2A fusion proteins were stably expressed in HeLa cells. The mCherry-H2A was used to mark mitotic chromosomes. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) FRAP curves of interphases and metaphases of YFP-Cbx2 and its variant fusion proteins expressed in HeLa cells. FRAP analysis is described in Figure 5. (D) Residence time and immobile fraction of YFP-Cbx2 variant fusion proteins at interphasic and mitotic chromatins. The residence time and immobile fraction were calculated from FRAP curves by fitting a first-order kinetic model.
