FIGURE 5:
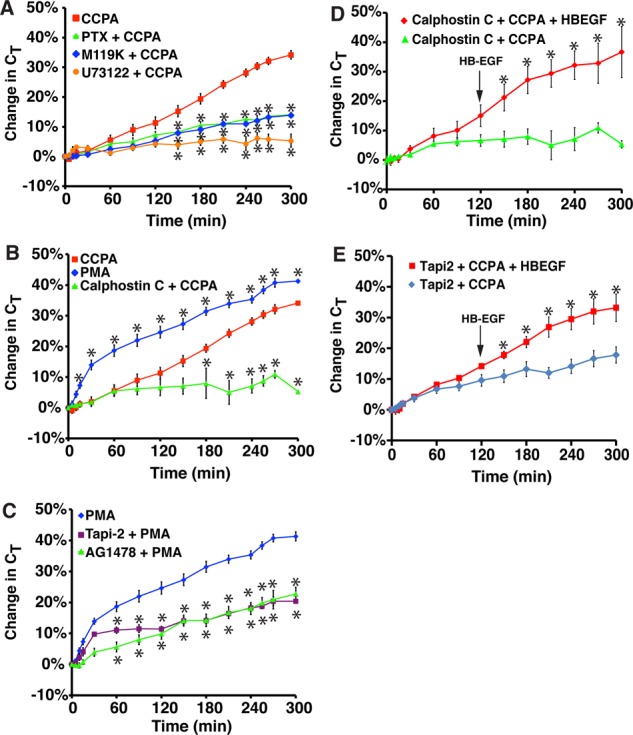
Role for Gi, Gβγ, PLC, and PKC in A1AR-stimulated exocytosis. (A) Rabbit tissue was left untreated or pretreated with 100 ng/ml pertussis toxin (PTX) for 90 min, 10 μM M119K for 60 min, or 10 μM U73122 for 60 min. CCPA (500 nM) was added to the mucosal hemichamber, and CT was recorded. (B) Rabbit tissue was left untreated or pretreated with calphostin C (500 nM) for 90 min. Subsequently, tissue was treated with CCPA (500 nM) or PMA (10 nM). (C) Rabbit tissue was pretreated with 15 μM Tapi-2 for 90 min or 1 μM AG1478 for 30 min and then treated with 10 nM PMA. The data for PMA treatment alone were reproduced from B. (A–C) Data for CCPA treatment alone were reproduced from Figure 1B. (D, E) Rabbit tissue was pretreated with calphostin C (D) or Tapi-2 (E) for 90 min, and then at t = 0, CCPA was added to the mucosal hemichamber. After 120 min, HG-EGF (1 nM) was added to the mucosal hemichamber (indicated with an arrow), and the tissue was incubated for additional 180 min. In D, data for calphostin C + CCPA are reproduced from B. (A–E) Data are presented as mean ± SEM (in A–C, n ≥ 3; in D and E, n ≥ 6). In A–C, values that are significantly different from CCPA alone (p < 0.05) are marked with an asterisk. In D and E, values that are significantly different from calphostin C + CCPA or Tapi-2 + CCPA (p < 0.05) are marked with an asterisk.
