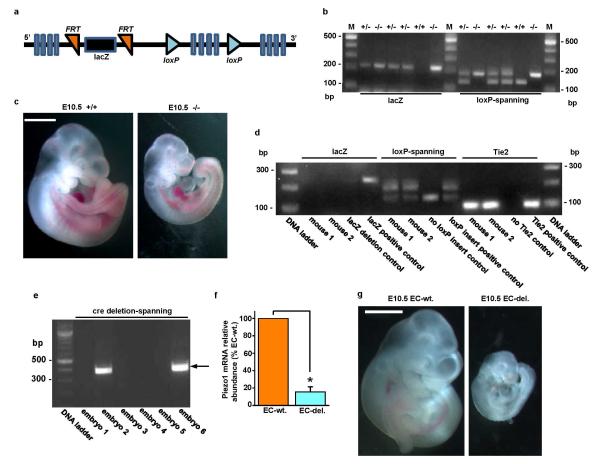
Extended Data Figure 3. Global and endothelial-specific Piezo1 modification and embryonic growth retardation in mice.
a, Simplified diagram of the Piezo1 Knockout First (conditional) construct provided in ES cells by the KOMP Repository (http://www.komp.org). Piezo1 is indicated containing insertion of lacZ sequence flanked by flippase recognition target (FRT) sites and downstream loxP sites. Further details of the construct can be obtained at http://www.komp.org. b-c, Global modification. b, Example genotyping results with lacZ or loxP-spanning PCR primers. M indicates the DNA marker ladder. On the left are results for 6 mice analysed by the lacZ PCR primers (expected product: 225 bp). On the right are the results for the same 6 mice analysed by primers targeted to endogenous Piezo1 sequence either side of the 3′ terminal loxP site (expected products: 155 bp without the loxP site; 189 bp with the loxP site). In the gel shown, 3 mice were heterozygous for the construct (+/−), 2 homozygous (−/−), and 1 wild-type (+/+). c, Images of example sibling E10.5 embryos. The embryo on the left was Piezo1+/+ and the embryo on the right was Piezo1−/−. The scale bar is 1 mm. d-g, Endothelial-specific modification. d, Example genotyping results for two mice (mouse 1 and mouse 2) both with deletion of the lacZ insert and transmission of Tie2-cre. Controls for the absence and presence of lacZ, the loxP insert, and Tie2-cre are included. Successful deletion of the lacZ insert was confirmed by lack of β-galactosidase staining (data not shown). e, Example genotyping results for six sibling embryos analysed with PCR primers spanning the deletion predicted to result from cre recombinase activity at the loxP sites. The forward primer was 5′ of the 5′ FRT site illustrated in (a) and the reverse primer was 3′ of the 3′ loxP site. The PCR product size after deletion was expected to be 379 bp. The product was detected in embryos 2 and 6. The PCR product was not generated in embryos without the deletion because it was too long to be amplified (4208 bp). Embryos exhibiting the 379 bp product were designated “EC-del.” to indicate disruptive deletion in Piezo1 of endothelial cells (ECs). Embryos designated as wild-type (wt.) exhibited no 379 bp product and only the 155 bp loxP product (as shown for the “no loxP insert control” in d). Out of a total of 142 embryos, 57 were EC-del. f, RT-PCR products detecting Piezo1 mRNA in total RNA from sibling embryos (Piezo1 3′ PCR primers) (n=3, each in duplicate). Piezo1 mRNA was significantly depleted in embryos displaying the 379 bp product described and shown in (e). g, Images of example sibling E10.5 embryos. The embryo on the left was wild-type and the embryo on the right contained endothelial-specific Piezo1 deletion (EC-del.). Retarded growth was apparent in EC-del. embryos and none of the other embryos. The scale bar is 1 mm. Error bars are s.e.m.