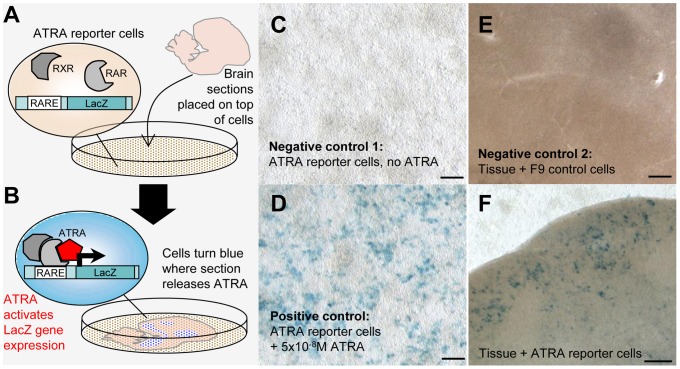
Figure 7. ATRA mapping in brain sections through a reporter cell assay.
A and B: Schematic overview of ATRA reporter cell assay. A: Reporter cells (they contain a LacZ gene under a retinoic acid response element, or RARE, and express retinoic acid and retinoid X receptors - RAR/RXRs - needed for ATRA induced gene expression) are seeded onto a Petri dish; a freshly cut brain section is placed into the dish and attaches to the cell monolayer. B: ATRA locally generated in the brain slice reaches a reporter cell, binds to RAR/RXR complexes and causes LacZ expression, revealed as blue label by LacZ/X-gal staining. C and D: LacZ expression in reporter cells is specifically induced by ATRA. C (negative control 1): In the absence of ATRA, reporter cells are LacZ-negative and do not turn blue upon LacZ/X-gal staining. D (positive control): Labeling is generated when ATRA is added to the medium. E (negative control 2): A slice co-cultured with an F9 cell line without RARE and LacZ does not generate blue signal upon LacZ/X-gal staining. F: A slice from an adult male bird co-cultured with reporter cells results in blue labeling in regions where ATRA is present. Blue labeling is seen under song nucleus HVC, which expresses zRalDH, but not in cells without overlying tissue (top), or in cells that underlie a part of the tissue that does not contain ATRA (bottom). Photos in C–F were taken through the bottom of the Petri dish. Scale bars: for C, D = 200µm; for E, F = 100µm.