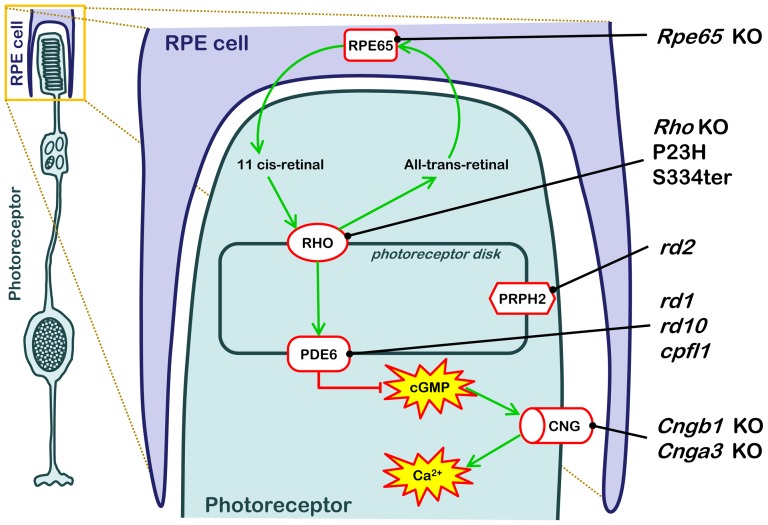
Figure 1. RD animal models used and their genetic defects.
The cartoon illustrates the anatomical localization and metabolic consequences of the causative genetic mutations in the ten different RD animal models used in this study. RD causing mutations in these animal models interfere with the various stages of the phototransduction cascade, from the 11-cis-retinal recycling enzyme RPE65 (Rpe65 KO), via the light-sensitive Rhodopsin (Rho KO, P23H, S334ter), cGMP-hydrolyzing phosphodiesterase-6 (PDE6; rd1, rd10, cpfl1), the structural protein Peripherin (Prph2; rd2), to the cyclic-nucleotide-gated (CNG; Cngb1 KO, Cnga3 KO) channel that allows for Ca2+-influx.