Figure 3. Functional considerations of different classes of co-released transmitters.
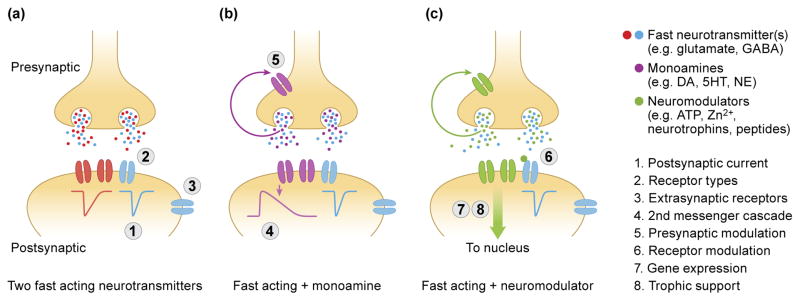
Different classes of dual-transmitter neurons have distinct functional implications for circuit dynamics. (a) The effect of neurons that release two fast-acting neurotransmitters (such as GABA and Glycine) is primarily determined by the postsynaptic receptors; including (1) the kinetics and amplitude of the postsynaptic current, (2) the specific receptor types expressed in the postsynaptic neuron and (3) the synaptic or extrasynaptic location of postsynaptic receptors. (b) For neurons that release a fast-acting neurotransmitter and a monoamine, additional factors that determine the functional output include (4) second messenger cascades and intrinsically slower currents, such as GIRK and (5) modulation of the presynaptic terminal. (c) The action of neurons that release a fast-acting neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator include (6) direct receptor modulation, (7) postsynaptic changes in gene expression and (8) trophic support.
