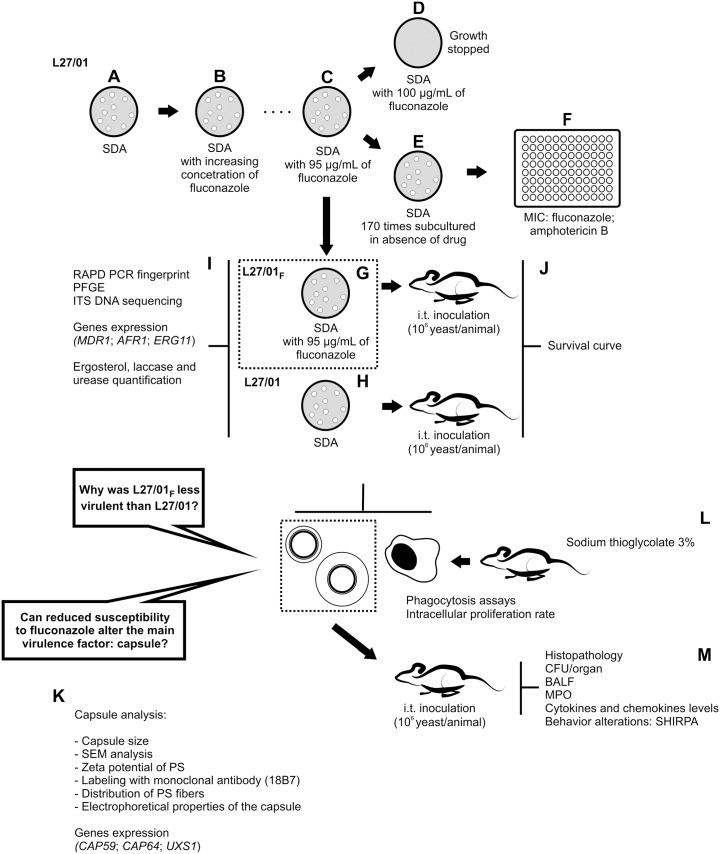
Figure 1. Synopsis of the methodology.
Fluconazole-resistant strain selection (A–F). After determining the MIC of fluconazole on SDA, an average of five colonies obtained from the highest fluconazole concentration were selected for culture on SDA plates supplemented with this drug. L27/01 (A) was the strain able to grow at the highest fluconazole concentration (B) and was chosen for culture on SDA plates supplemented with this drug. This strain was cultured in solid medium with increasing concentrations (B–C) of fluconazole until growth ceased at 100 µg/mL (D). To verify the maintenance of resistance to fluconazole and cross-resistance between this drug and amphotericin B, the selected strain was cultured in SDA without drug every 48 h 170 times (E), and the MIC test was performed by microdilution every 5 subcultures (F). Colonies grown at 95 µg/mL were maintained in this concentration, and the strain was named “L27/01F” (G). L27/01 strain grew in the absence of drug (H). The genetic similarity between L27/01 and L27/01F strains was evaluated by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD)-PCR, PFGE and ITS Sequencing. CAP59, CAP64, ARF-1, ERG11, UXS-1 levels by real-time PCR were evaluated. Lipid evaluation was performed to compare the ergosterol content of L27/01 and L27/01F cell membranes. Also, Urease and Laccase activities of L27/01 and L27/01F strains were determined (I). Evaluation of murine cryptococcosis after inoculation with L27/01 or L27/01F strain: survival curve (J). Investigation of whether fluconazole affects the polysaccharide (PS) capsule (K). The phagocytosis assay was performed to assess the influence of PS capsules from L27/01 and L27/01F strains on phagocytosis and intracellular proliferation rate (IPR) in murine peritoneal macrophages from C57BL/6 mice (L). Cryptococcal cell dissemination, immune response and behavioral alterations (M). SDA: Sabouraud Dextrose Agar. MIC: Minimum inhibitory concentration. PFGE: Pulsed field gel electrophoresis. CFU: Colony forming units. BALF: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. MPO: Myeloperoxidase activity. i.t.: intratracheal infection. PS: polysaccharide.