Figure 4.
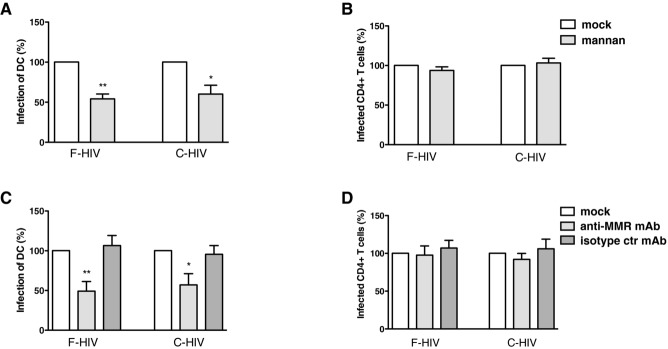
Blockade of the C-type lectin MMR decreases the infection of DCs emigrating out from cervical tissues. The cervical tissue biopsies were pretreated for 30 min at min 37°C with mock, mannan, anti-MMR mAb, or isotype control mAb followed by infection with different forms of HIV-1BaL, either free (F-HIV) or complement opsonized (C-HIV), by spinning the cultures for 2 h at 37°C. The tissues were washed and transferred to six-well plates and cultured for 3–6 days with mock, mannan, anti-MMR mAb, or isotype control mAb. The emigrating cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD1a, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for DCs and anti-CD3, anti-CD4, and anti-HIV-1 mAbs for CD4+ T cells and level of infection was assessed by flow cytometry. (A, B) The level of HIV-1 infection in (A) DCs (N = 4–5) or (B) T cells (N = 3) in the different experiments treated with mock or mannan was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. (C, D) The level of HIV-1 infection in (C) DCs (N = 4–7) or (D) T cells (N = 4–9) in the different experiments treated with mock, anti-MMR mAb, or isotype control mAb was normalized with F-HIV set as 100%. Statistical significance was tested using a two-sided paired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. Data are shown as mean + SEM of the indicated number of samples, each assessed in its own experiment.
