Fig. 6.
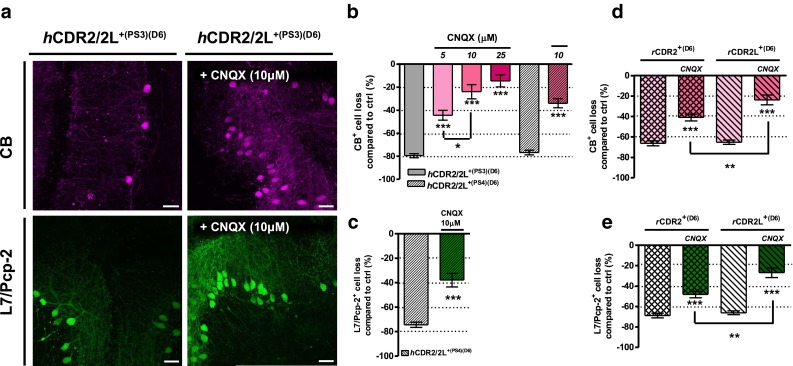
Indirect blockage of VGCC via AMPA receptor blockage attenuated rCDR-induced pathology. a z-stack multiphoton micrograph: indirect blockage of VGCC activity by blocking AMPAR activity with CNQX inhibits the observed hCDR2/2L+(PS3)-induced loss of CB (magenta) and L7/Pcp-2 (green) (right vs. left panel) (hCDR2/2L +(PS3): 4 μL/mL, CNQX: 10 μM; sample: day 6); scale bars 40 μm. Stereological counting of CB+ (b, d) and L7/Pcp-2+ (c, e) PCs showed that CNQX co-treatment reduced the hCDR2/2L- (4 μL/mL; CNQX: 5, 10, 25 μM; PS3: n E = 6; PS4: n E = 4) or rCDR-induced pathology (125 ng/mL, 10 μM, n E = 6) in a concentration-dependent manner and more beneficially for rCDR2L than rCDR2 (CB: **p = 0.0071; L7/Pcp-2: **p = 0.0011). Data are mean ± SEM. Non-parametric two-tailed paired Mann–Whitney’s U test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; # p < 0.005; Table 1: CDR antibody effects in percentage
