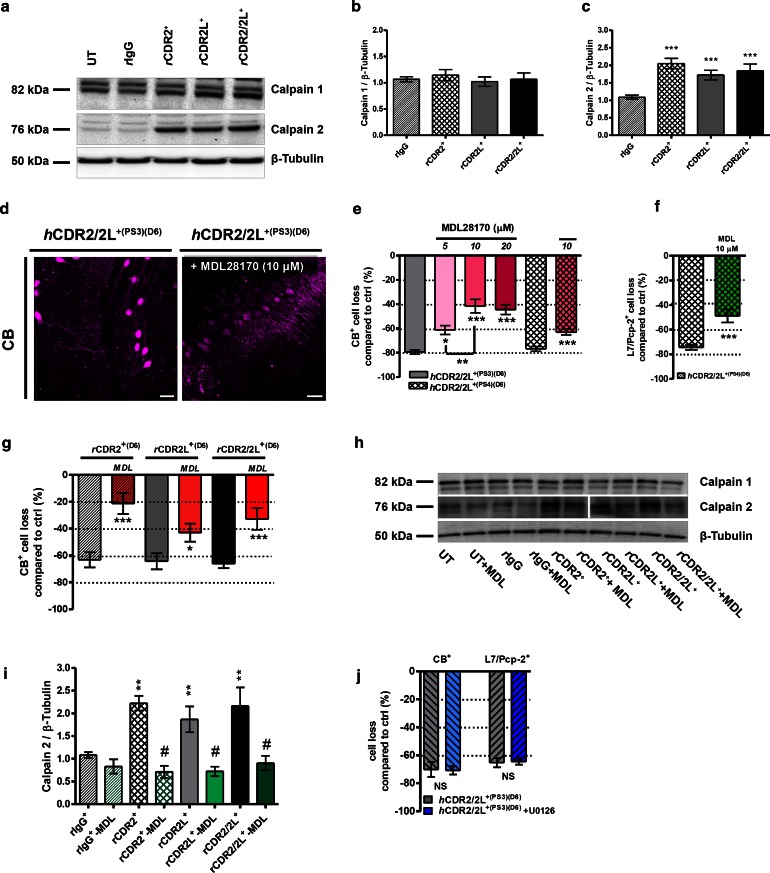
Fig. 8.
Calpain-2 activity is increased by CDR-Ab internalization, but not MAP kinase. a Representative Western blot: calpain-1 and calpain-2 expression after rCDR internalization and MDL28170 co-treatment (h). b Bar plots show that calpain-1 expression is not affected, but c calpain-2 expression is significantly increased after rCDR internalization (125 ng/mL; D6; n E = 21) and can be i blocked by co-treatment with calpain antagonist MDL28170 (125 ng/mL + 10 μM MDL28170; n E = 5). Calpain antagonist MDL28170 reduced the CDR-induced CB+ and L7/Pcp-2+ PC loss. d z-Stack multiphoton micrographs: co-treatment with calpain antagonist MDL28170 (10 μM) beneficially affects PC anti-CB (magenta) staining after hCDR2/2L+(PS3) internalization (4 μL/mL, 6 days); scale bars 40 μm. Stereological counting of CB+ (e) and L7/Pcp-2+ (f) cells/mm3 in these micrographs showed that hCDR2/2L+(PS3)/MDL28170 treatment (5, 10, 20 μM) reduced the CDR-induced loss of CB [n E = 6 (PS3) and n E = 4 (PS4)] and L7/Pcp-2 [nE = 3 (PS4)]. g Similar observation was found for rCDR/MDL28170 co-treatment (125 ng/mL, 10 μM MDL28170, CB: n E = 5). Calpain antagonist reduced the CDR-induced loss depending on the CDR target to up to 60 % (Table 1). This was most pronounced for CDR2. j MAP kinase antagonist U0126 (5 μM) does not influence the loss of CB+ or L7/Pcp-2+ PCs after hCDR2/2L+(PS3) internalization (1 μL/mL; 6 days; n E = 4). Data are mean ± SEM. Non-parametric two-tailed paired Mann–Whitney’s U test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; # p < 0.008. Table 1: CDR antibody effects in percentage