Figure 1. Most DR neurons projecting to the VTA express VGluT3 mRNA.
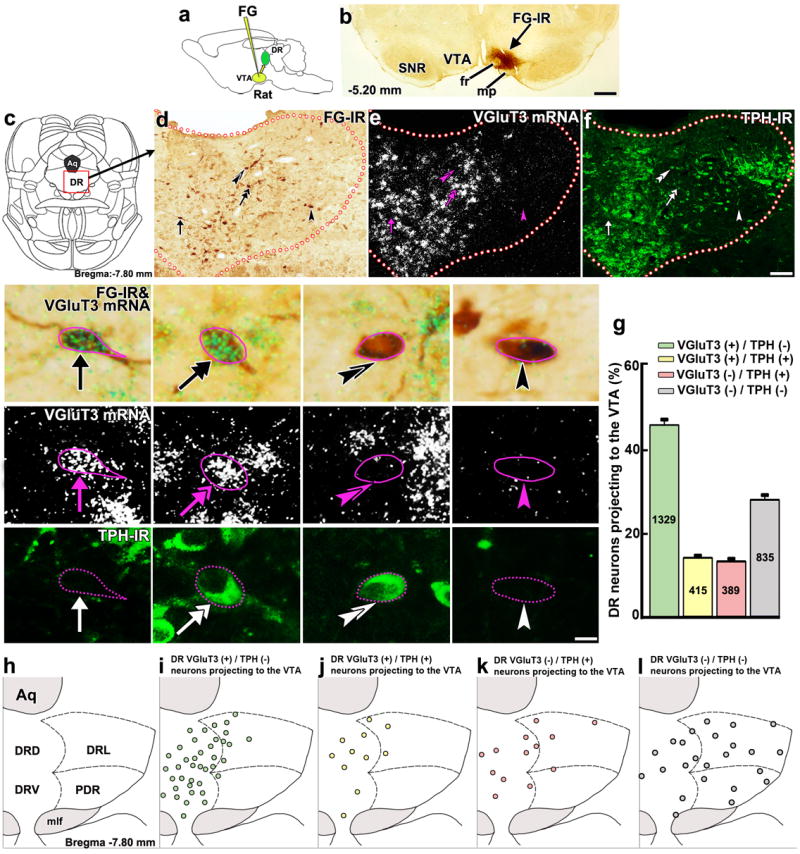
(a) Retrograde tracer FG was delivered into the VTA. (b) FG injection site in the VTA. (c) DR diagram. (d-f) Low magnification of a DR coronal section showing brown cells with FG-immunoreactivity (FG-IR, d), expression of VGluT3 mRNA (white aggregated grains; e) or TPH-immunoreactivity (TPH-IR, green; f). Four individual cells are seen at higher magnification. A FG neuron expressing VGluT3 mRNA without TPH-IR (arrow), a FG neuron co-expressing VGluT3 mRNA and TPH-IR (double arrow), a FG neuron expressing TPH-IR only (double arrowheads) and a FG neuron lacking both VGluT3 mRNA and TPH-IR (arrowhead). (g) Frequency of FG phenotypes (mean + s.e.m.). Among all DR neurons projecting to the VTA, 46% expressed only VGluT3 mRNA, 14% co-expressed VGluT3 mRNA and TPH-IR, 13% expressed TPH-IR alone, and 28% lacked both VGluT3 mRNA and TPH-IR. FG cell counting was made between bregma -6.84 and -8.40 mm (n = 4, 10-15 sections per rat). (h-l) Phenotype map of DR neurons projecting to the VTA. Each dot represents the average of DR neurons projecting to the VTA. Many VGluT3 expressing neurons without TPH-IR were concentrated in the dorsal part (DRD) and ventral part (DRV) of the DR (green; i) intermixed with neurons that either co-expressed TPH-IR with VGluT3 (yellow; j) or expressed only TPH-IR (pink; k). DR neurons projecting to the VTA lacking both VGluT3 and TPH-IR were frequently observed in the DRD, DRV, lateral (DRL) and posterodorsal (PDR) aspects of the DR (grey; l). Aq, aqueduct; fr, fasciculus retroflexus; mlf, medial longitudinal fasciculs; mp, mammillary peduncle; SNR, substantia nigra reticulata. Diagrams were adapted from rat brain atlas57. Bars: (b) 400 μm; (f) 110 μm; 10 μm for high magnification.
