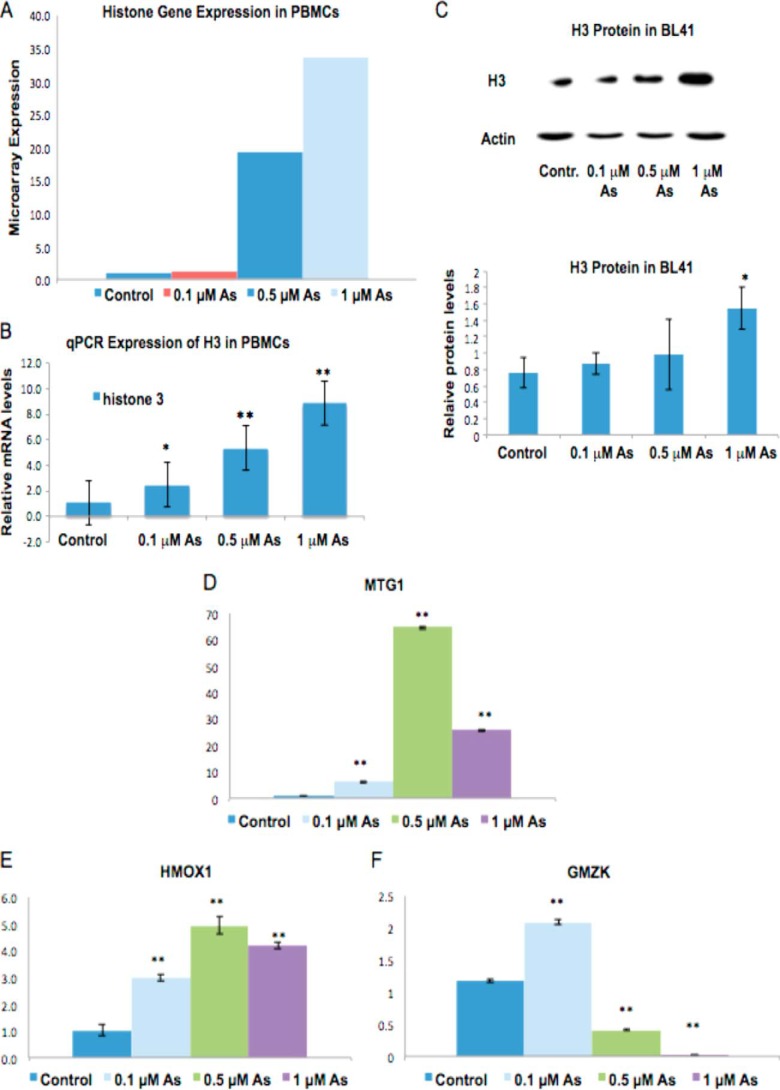
FIGURE 1.
Canonical histone gene transcription and H3 protein levels are increased by arsenic. A, total RNA was extracted from PBMCs after a 48-h treatment with 0, 0.1, 0.5, or 1 μm arsenic. Representative Affymetrix microarray -fold changes in the expression of canonical, replication-dependent histone genes are shown. B and D–F, mRNA levels of H3.1 (B), MTG1 (D), HMOX1 (E), and granzyme K (GMZK) (F) were analyzed by quantitative RT-qPCR. Relative mRNA levels were normalized to 18 S rRNA expression and are presented as -fold change to the level expressed in PBMCs. Data are mean ± S.D. (n = 3). C, BL41 cells were treated with 0, 0.1, 0.5, or 1 μm of arsenic for 48 h. Cells were lysed with radioimmune precipitation assay buffer, and whole-cell lysate was run on 15% SDS acrylamide gels. Upper panel, representative Western blot of H3 protein in BL41 cells. Lower panel, quantification of H3 protein levels in BL41. Relative protein levels were calculated based on band intensity measured with ImageJ software. Statistical significance was calculated using an unpaired, two-tailed t test with * indicating a p value less than 0.05 and ** indicating a p value less than 0.01. Error bars represent S.D.