FIGURE 6.
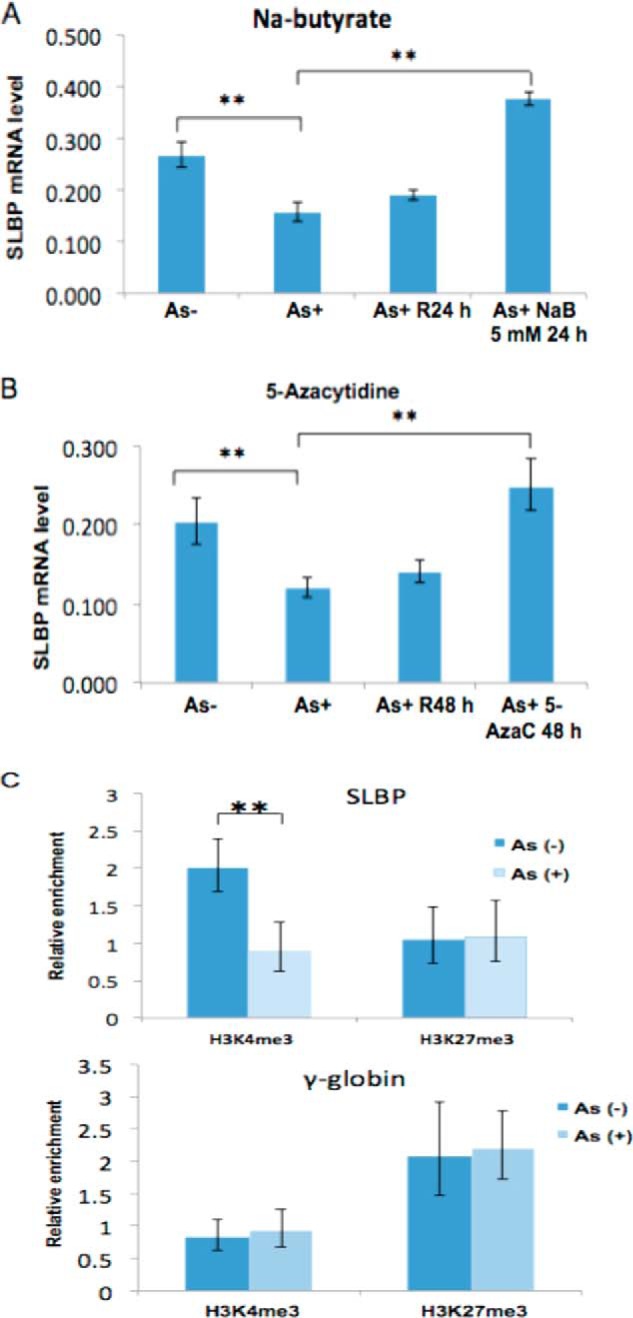
Arsenic down-regulates SLBP mRNA via epigenetic mechanisms. A, arsenic-induced reduction of the SLBP mRNA level was rescued by inhibitors of histone acetylation. After treating BEAS-2B cells with 1 μm arsenic for 48 h, the cells were recovered in arsenic-free medium, treated with or without 5 mm sodium butyrate (NaB) for 24 h, and subjected to RT-qPCR using SLBP primers. γ-Tubulin was used as an internal control. R24 h, cells cultured in regular medium without sodium butyrate. B, arsenic-induced reduction of the SLBP mRNA level was rescued by inhibitors of DNA methylation. After treating BEAS-2B cells with 1 μm arsenic for 48 h, the cells were recovered in arsenic-free medium treated with or without 10 μm 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine for 48 h and subjected to RT-qPCR using SLBP primers. γ-Tubulin was used as an internal control. R48 h, cells cultured in regular medium without 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (AzaC). C, ChIP analysis of the SLBP promoter region. Mono- and dinucleosomes were purified by sucrose gradient from arsenic-treated and untreated BEAS-2B cells, and ChIP assays were performed. Levels of the active histone mark H3K4me3 at the SLBP promoter region were decreased by more than 50% after arsenic treatment, whereas H3K27me3 remained unchanged. γ-Globin was used as a negative control. Statistical significance was calculated using an unpaired, two-tailed t test with * indicating a p value less than 0.05 and ** indicating a p value less than 0.01. Error bars represent S.D.
