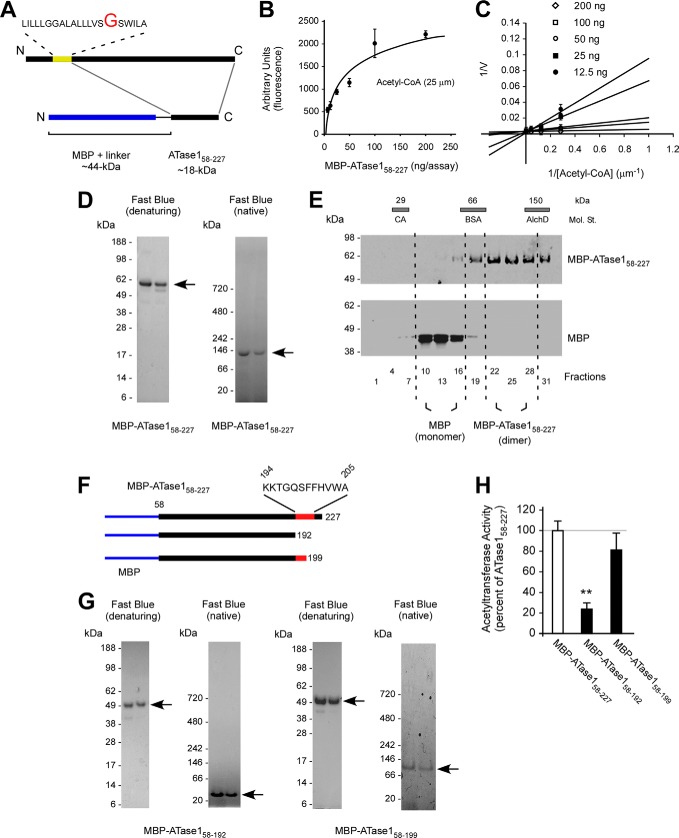
FIGURE 3.
The dimerization of the ATases occurs through the C terminus. A, schematic view of the MBP-ATase1 fusion protein (referred to as MBP-ATase158–227). The membrane domain of ATase1 is shown in yellow. B and C, MBP-ATase158–227 retains acetyl-CoA:lysine acetyltransferase activity. The transfer activity of the fusion protein at 25 μm concentration of acetyl-CoA ranged between 80 and 300 pmol/min/ng of enzyme. D, MBP-ATase158–227 migrates as a dimer under native conditions. E, MBP-ATase158–227 migrates as a dimer on sedimentation gradients. E, molecular standards (Mol. St.) were run in parallel; their sedimentation profile is shown as bars on top. CA, carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa); BSA, bovine serum albumin (66 kDa); AlchD, alcohol dehydrogenase (150 kDa). F, schematic view of the C-terminal deletions used to generate MBP-ATase158–192 and MBP-ATase158–199 fusion proteins. The domain predicted to be involved in the dimerization is shown in red. MBP is shown in blue. G, MBP-ATase158–192 migrates as a monomer under native conditions. H, acetyltransferase activity of the different MBP-ATase1 fusion proteins tested here. MBP-ATase158–192 displays reduced activity. The values are the averages (n = 5) ± S.D. **, p < 0.005.