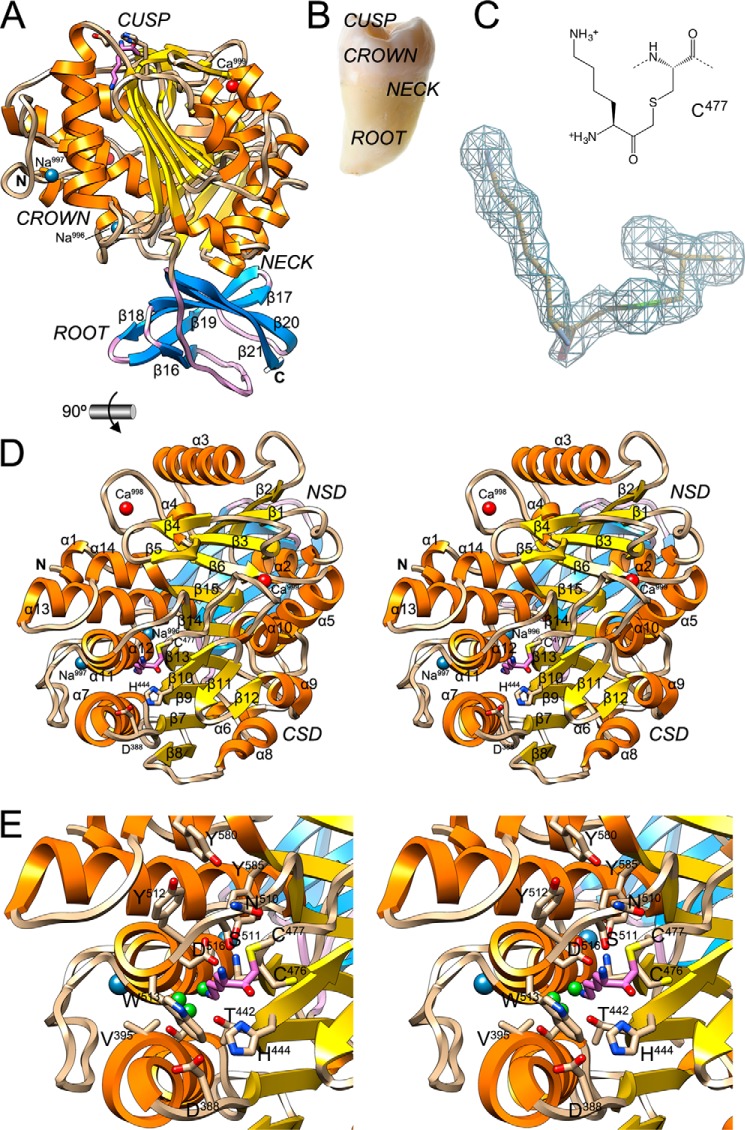
FIGURE 2.
General architecture of KgpB. A, ribbon-type plot of Kgp(CD+IgSF) showing the regular secondary structure elements (CD, α-helices as orange ribbons, β-strand as yellow arrows, and coils in tan; IgSF, β-strand as blue arrows labeled β16–β21 and coils in lilac). The N and C termini and the four structural cations (calciums Ca999 and Ca998 in red and sodiums Na997 and Na996 in blue) are depicted. The (putative) catalytic triad, Cys477 (covalently modified at Sγ with an l-lysinylmethyl group; carbons in lilac), His444, and Asp388, is further shown as sticks. Black arrows point to the solvent channel (see Fig. 3D). B, picture of a tooth with its parts labeled. C, (2mFobs − DFcalc)-type Fourier map of the region around the catalytic cysteine Cys477 obtained with diffraction data to 1.75-Å resolution and contoured at 1σ above threshold. D, structure of Kgp(CD+IgSF) in cross-eye stereo in standard orientation (28, 79), which corresponds to a horizontal 90° rotation of the view in A, i.e. viewing the CD cusp region. Regular secondary structure elements of the CD (helices α1–α14 and strands β1–β15) are labeled. The NSD is on top, and the CSD is at the bottom (see also Fig. 5D). E, close-up of D in stereo centered on the non-primed side of the active site. Residues framing the specificity pocket S1 and pocket S2 are labeled. Small green spheres represent solvent molecules.