Figure 1.
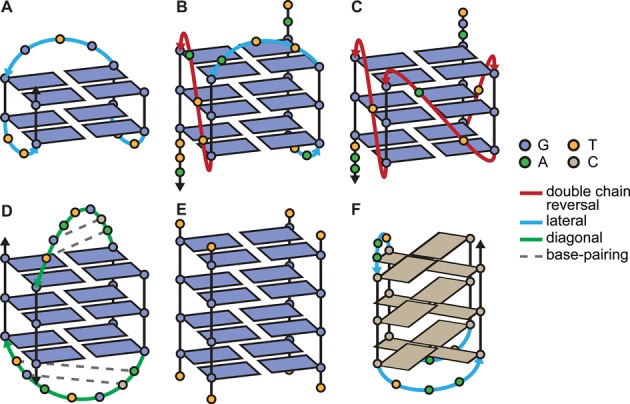
Schematic secondary structures of some of the quadruplex-forming sequences used in this study: TBA (A), 25TAG (B), c-myc (C), H-Bi-G4 (D), [TG4T]4 (E) and the i-motif 21CC (F). Intra- and bi-molecular structures exhibit different loop lengths (2–7) and conformations (see color legend), number of quartets (2–4), relative strand orientation (A, D: antiparallel; C, E: parallel; B: hybrid 3+1) and molecularity (A, B, C: monomolecular, D: bimolecular, E: tetramolecular). H-Bi-G4 displays very particular loops that form short duplex hairpins, while the human telomeric sequence (25TAG) is one example of polymorphism dependent on termini sequence changes and experimental conditions. Cations and glycosidic bond angles are not shown for the sake of clarity. A more accurate depiction of these structures, and others, can be found in Supplementary Figure S1.
