Figure 5.
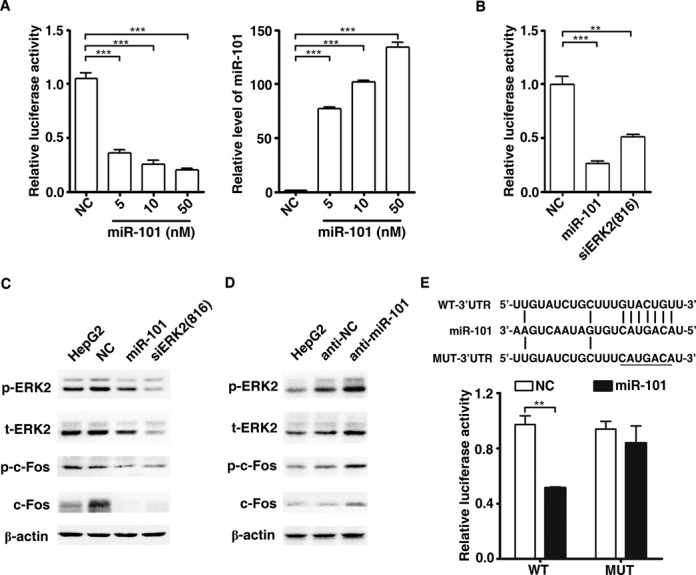
MiR-101 suppresses AP-1 activity by targeting c-Fos and ERK2. (A) Overexpression of miR-101 inhibited the transcriptional activity of AP-1 in dose-dependent manner. Left panel: miR-101 suppresses the transcriptional activity of AP-1. Right panel: overexpression effect of miR-101. HepG2 cells were reverse transfected with miR-101 duplex for 24 h, followed by co-transfection with pAP-1-Luc and pRL-PGK plasmids. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h after the transfection of plasmids. All the cells were treated with 40 ng/ml TPA for 4 h before luciferase assay. ***P < 0.001. (B) Either ERK2 knockdown or miR-101 overexpression suppressed the transcriptional activity of AP-1. Experiment was performed as described in (A). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) miR-101 reduced the levels of cellular c-Fos and ERK2 proteins. Whole cell extracts were prepared from HepG2 cells that had been transfected with the indicated RNA duplexes for 46 h then treated with DMSO or 40 ng/ml TPA for 2 h. β-actin was used as internal control. (D) Inhibition of miR-101 increased the expression of c-Fos and ERK2 proteins. HepG2 cells were non-transfected or transfected with the inhibitor of miR-101 (anti-miR-101) or its control (anti-NC) for 44 h, and then treated with TPA for 4 h before protein extraction. (E) MiR-101 regulated gene expression by binding to the sequence in the 3′UTR of ERK2. Upper, putative miR-101 binding sequence in the 3′UTR of ERK2 mRNA. Mutation was generated on the potential seed sequence (underlined), as indicated. HepG2 cells were co-transfected with NC or miR-101 duplex, and the luciferase reporter plasmid containing wild-type (WT) or mutant (MUT) ERK2 3′UTR. The normalized luciferase activity of NC transfectant in one experiment was set as relative luciferase activity 1. **P < 0.01.
