Figure 7.
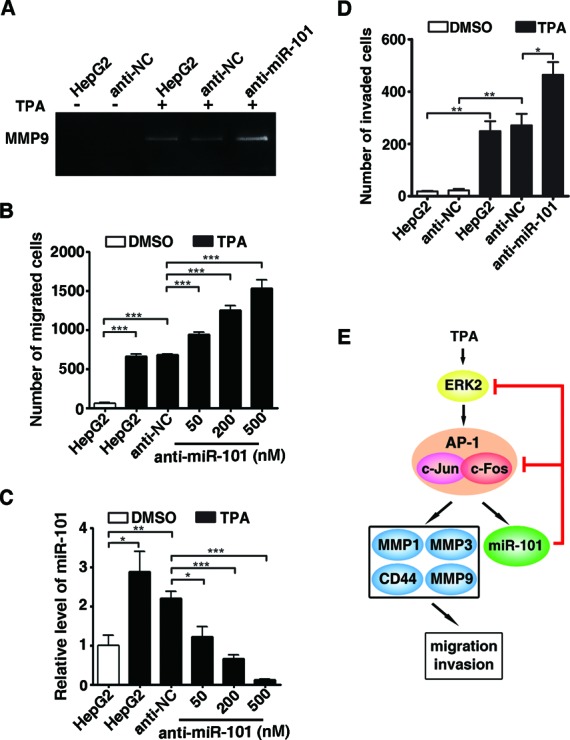
Disruption of the miR-101/AP1 feedback loop promotes the TPA-induced migration and invasion. (A) Inhibition of miR-101 increased the TPA-induced MMP9 activity. HepG2 cells without transfection or transfected with anti-miR-101 or anti-NC were treated with or without TPA for 24 h, and then incubated in the serum-free DMEM for 20 h, followed by gelatin zymography assay. (B) Antagonism of miR-101 increased the TPA-induced migration in a dose-dependent manner. (C) Knockdown effect of anti-miR-101. (D) Antagonism of miR-101 increased the TPA-induced invasion. In (B) and (D), HepG2 cells without transfection or transfected with anti-miR-101 or anti-NC were treated with or without TPA for 24 h, and then added to transwell chambers for 20 h, followed by analysis for migration (B) and invasion (D). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. (E) Schematic diagram showed the AP-1/miR-101 regulatory feedback loop.
