Figure 5.
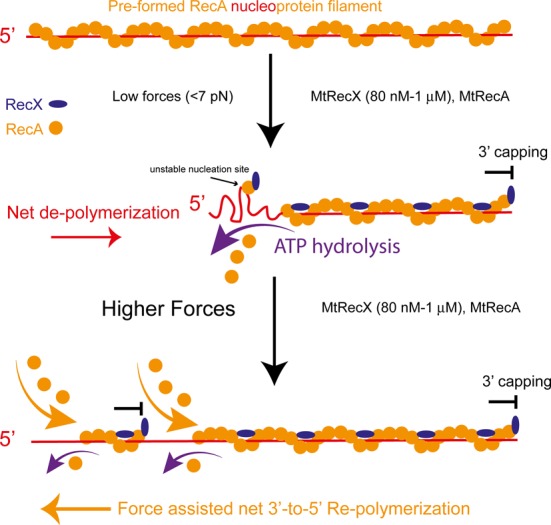
Mechanistic model of the effects of force on MtRecX-dependent MtRecA filament dynamics. A preformed MtRecA filament (orange) on ssDNA (red) is capped by MtRecX (blue) at its 3′ end (based on the 3′ capping model proposed by Dress et al. (11)) and is bound with MtRecX at the filament grooves (based on electronic microscopy reconstruction (14)). At low forces (<7 pN according to our measurement), MtRecA dissociates from the ssDNA at the 5′ end that requires ATP hydrolysis, resulting in net de-polymerization. Any potential new nucleation sites formed on the vacated ssDNA are not stable since MtRecX caps them at the 3′ end. At higher forces (>7 pN), due to the stabilizing effect of force on RecA filament, a partially de-polymerized MtRecA filament may re-polymerize from the 5′ end of the remained filament and/or from the new nucleation sites in a force assisted 3′-to-5′ reverse direction.
