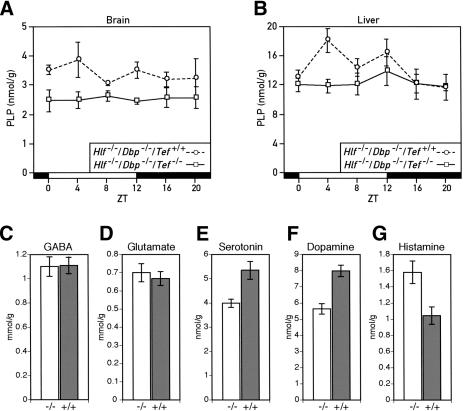
Figure 5.
Down-regulation of pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) levels and dysregulation of neurotransmitter metabolism in PAR bZip triple-knockout mice. (A) Temporal concentration of PLP in the brains of double- and triple-knockout mice. The PLP levels were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of perchloric acid brain extracts prepared from animals sacrificed at the indicated Zeitgeber times (ZT). The values are means ± S.E.M. from three animals. The difference between the two genotypes is highly significant (ANOVA F[1,32] = 20.18, p < 1.10-4). (B) Temporal accumulation of PLP in the livers of double- and triple-knockout mice. PLP levels were determined as in A, and the values are means ± S.E.M. from at least six animals. ANOVA revealed significant circadian rhythmicity in PLP levels in double-knockout animals (F[5,32] = 2.60, p < 0.05). The difference between geno-types is also statistically significant (ANOVA F[1,73] = 5.31, p < 0.025). (C,D) GABA (C) and Glutamate (D) concentration in the brains of Hlf-/-/Dbp-/-/Tef-/- (-/-) and Hlf-/-/Dbp-/-/Tef+/+ (+/+) mice. No statistically significant difference could be found between the two genotypes. The values are means ± S.E.M. from 12 animals of each genotype. (E,F,G) Concentration of serotonin (E), dopamine (F) and histamine (G) in the brains of Hlf-/-/Dbp-/-/Tef-/- (-/-) and Hlf-/-/Dbp-/-/Tef+/+ (+/+) mice. The difference between genotype is statistically significant (Student's t test: p < 0.005 for serotonin, p < 0.0001 for dopamine and p < 0.01 for histamine). The values are means ± S.E.M. from 12 animals of each genotype.