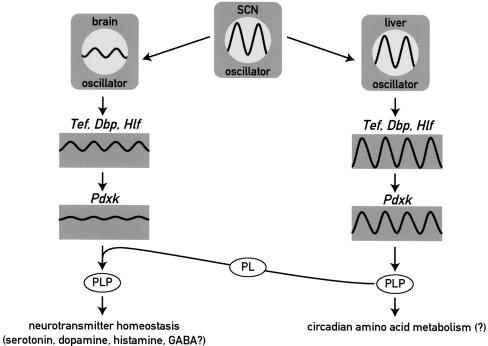
Figure 7.
Model showing the regulation and function of Pdxk in brain and liver. The molecular circadian oscillator generates high amplitude cycles and low amplitude cycles of PAR bZip gene expression in liver and brain, respectively. Accordingly, target genes of PAR bZip transcription factors, such as Pdxk, are expressed in a strongly circadian manner in liver and at nearly constant levels in the brain. As PLP, the product of the PDXK reaction is a coenzyme for amino acid decarboxylases and aminotransferases, the rhythmic production of PLP in the liver may contribute to circadian amino acid metabolism. In the brain, nearly invariable Pdxk expression may be essential for regulating neurotransmitter homeostasis, as moderate decreases in PLP levels may result in neurotransmitter deficiencies and epileptic attacks (see text). (SCN) suprachiasmatic nucleus harboring the central circadian pacemaker; (PLP) pyridoxal phosphate; (PL) pyridoxal.