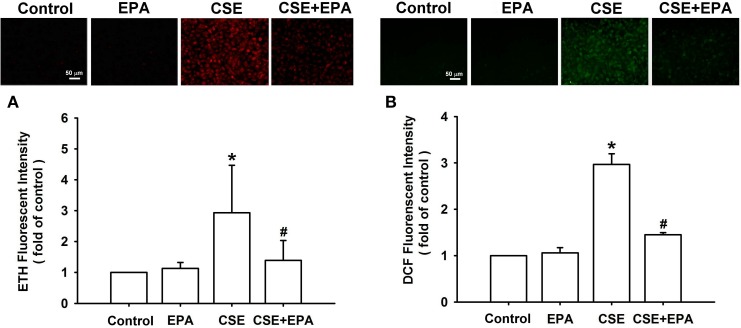
Figure 5.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) attenuates increases in intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced by cigarette smoke extract (CSE) in human bronchial epithelial cells. Cells were exposed to medium alone or 3% CSE for 30 min with pretreatment with EPA (5 μM) or its vehicle. After exposure, the cells were collected for the measurement of intracellular ROS levels. Levels of ROS were measured by HE/ETH (A) and DCFH-DA/DCFH (B) fluorescent probes. Data in each group are mean ± s.e.m. from five independent experiments. *p < 0.05 vs. control (vehicle without CSE stimulation). #p < 0.05 vs. CSE without EPA pretreatment.