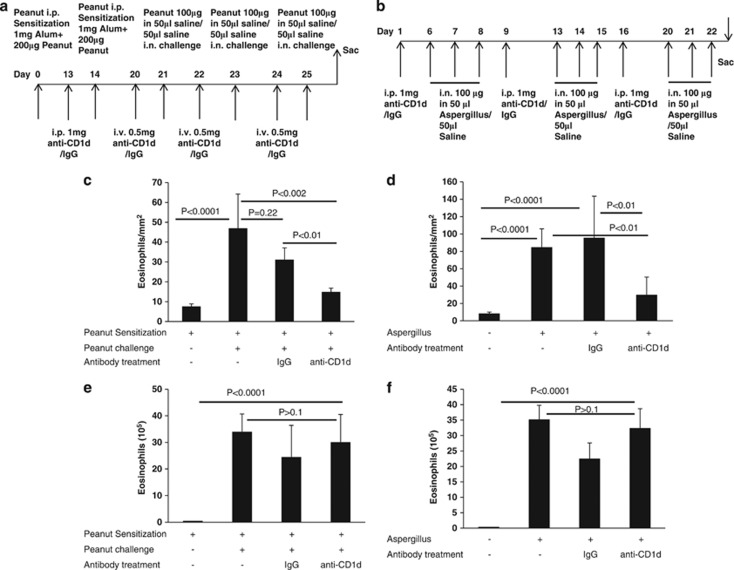
Figure 6.
iNKT neutralization protects mice from food- and aeroallergen-induced experimental EoE. The Balb/c mice were subjected to iNKT cell neutralization by injecting the anti-CD1d monoclonal antibody or isotype-matched IgG in an allergen-induced mouse model of EoE as per the protocol (a, b). The number of eosinophils in the esophagus was analyzed in the food allergen-sensitized mice treated with anti-CD1d or IgG and challenged with saline (−) or peanut (+) is shown following 24 h after last saline or peanut challenge (c). Data are expressed as mean±s.d., n=9–12 mice/group. The anti-CD1d or IgG treated and intranasally challenged with saline (−) or aeroallergen (Aspergillus fumigatus; +) were also examined for esophageal eosinophilia and are shown as eosinophils/mm2 following 20 h after last Aspergillus or saline challenge (d). Data are expressed as mean+s.d., n=12 mice/group. The eosinophil numbers in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were counted in food allergen-sensitized mice treated with anti-CD1d or IgG and challenged with saline (−) or peanut (+) and CD1d-treated and challenged with saline or Aspergillus (e and f). Statistical significance was calculated using both the Mann–Whitney and Kruskal–Wallis test, and the significance levels are shown in respective figures.