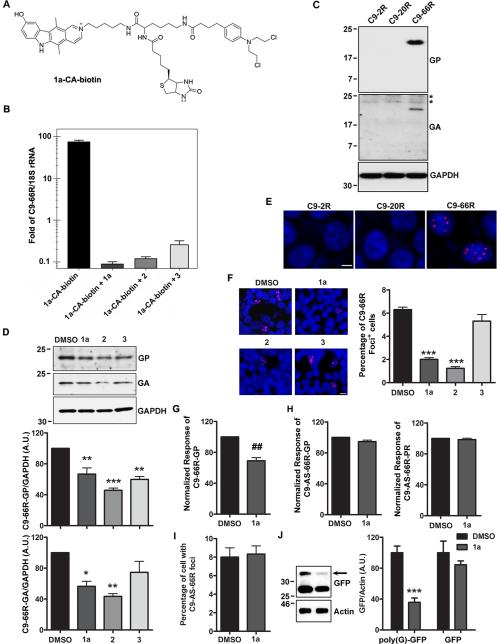
Fig. 2. Small molecules targeting r(GGGGCC) inhibit RAN translation and foci formation in (GGGGCC)66-expressing cells.
A) Structure of 1a-CA-biotin; the chlorambucil moiety (CA) forms a covalent bond with the cellular target once the small molecule is bound. Biotin is used to isolate biomolecule-small molecule adducts from cells. B) Normalized enrichment of r(GGGGCC)66 from biomolecules isolated with streptavidin beads as compared to 18S rRNA determined by qRT-PCR. Cells were treated with 1a-CA-biotin alone or with 1a, 2 or 3 (competitive profiling). In competitive profiling experiments, the unreactive compound inhibits reaction of the target with 1a-CA-biotin and thus the target is depleted in pull-down fractions. Data presented as mean±SD (n=2). C) Cells overexpressing 66 (GGGGCC) repeats (C9-66R), but not 2 (C9-2R) or 20 (C9-20R), express poly(GP) and poly(GA) proteins. Asterisks demark non-specific bands. D) Western blot and densitometry of poly(GP) and poly(GA) proteins in (GGGGCC)66-expressing cells treated with DMSO or compounds 1a, 2 or 3 (100 μM, 24 h). Data represents mean+SEM (n=3). E) RNA foci (red) are detected in the nucleus (Hoechst; blue) of C9-66R cells. F) Evaluation of the percentage of foci-positive cells by RNA FISH post-treatment. Data represents mean+SEM in 10 fields. G-H) Compound 1a decreases RAN translation of poly(GP) proteins from sense (GGGGCC)66 repeats in C9-66R cells (G), but does not influence levels of poly(GP) or poly(PR) proteins RAN translated from antisense (CCCCGG)66 repeats in C9-AS-66R cells (H), as assessed by GP and PR immunoassays. Data represents mean+SEM (n=3 or 4). I) The percentage of r(CCCCGG)-containing foci in C9-AS-66R cells is not affected by 1a. J) 1a decreases RAN translation of poly(G) in cells expressing (CGG)88 upstream of GFP. Data presented as mean+SEM (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, as assessed by One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's Multiple Comparison Test. ##P<0.01, as assessed by t-test. See also Figure S2.