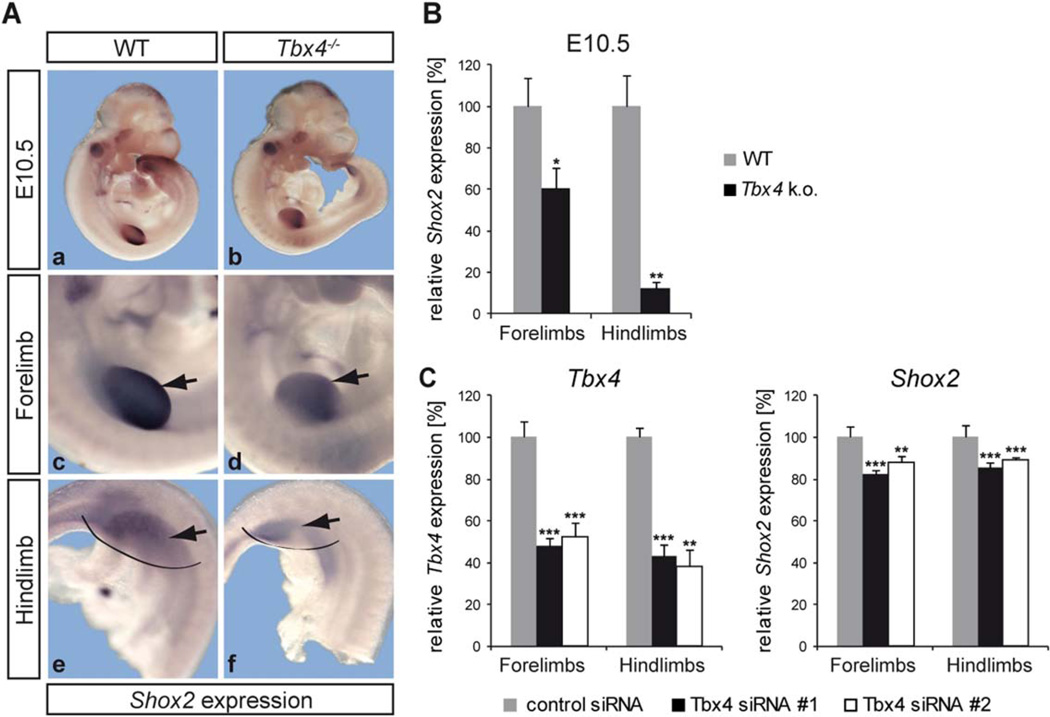
Fig. 4.
Shox2 is downregulated in Tbx4−/− fore- and hindlimbs. A: Whole mount in situ hybridization on E10.5 WT and Tbx4−/− embryos using a Shox2 RNA probe shows a decreased Shox2 expression in both fore- (d) and hindlimbs (f) of Tbx4−/− embryos (indicated by arrows). N = 7; limbs in a, b are magnified in c–f. B: Results were confirmed by qRT-PCR using WT and Tbx4−/− limb tissue. Tbx4 knockout leads to a ∼40% decrease of Shox2 mRNA in forelimbs and a ∼85% decrease in hindlimbs; *P <0.05, **P <0.01; n = 3 independent experiments performed with 2–3 pooled embryos of 2 litters; grey bars indicate relative Shox2 mRNA levels in WT, black bars relative Shox2 levels in Tbx4−/−C:Tbx4 knockdown in primary fore- and hindlimb cells. Transfection with 2 different Tbx4 siRNAs (#1, #2), in parallel with a control siRNA, results in a ∼50–60% reduction of Tbx4 mRNA levels after 24 hr (left), leading to a ∼10–20% downregulation of Shox2 (right) in fore- and hindlimb cells; **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001; n = 10 for siRNA #1, n = 7 for siRNA #2; grey bars show relative Tbx4/Shox2 mRNA levels after control siRNA transfection; black and white bars relative Tbx4/Shox2 mRNA levels after Tbx4 siRNA transfection.