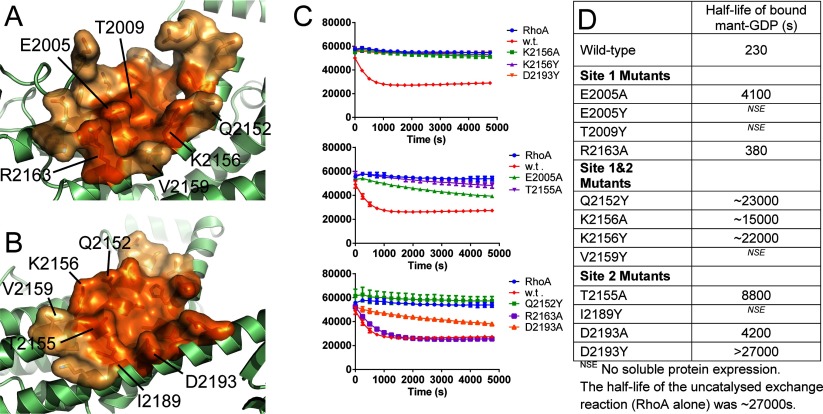
Figure 6. Surface pockets on the AKAP-Lbc DH domain are potentially suitable for binding of protein–protein interface inhibitors.
(A) Site 1 which binds the switch I loop of RhoA. (B) Site 2 which binds the switch II loop of RhoA. The core of each pocket containing the residues in direct contact with RhoA is coloured dark orange, whereas the surrounding region of the pocket is coloured light orange. Sites of mutations made are indicated (C). Nucleotide-exchange assays for DH domain mutants compared with wild-type. (D) Approximate half-lives of RhoA–MANT-GDP based on fitting the curves in (C) to an exponential decay.