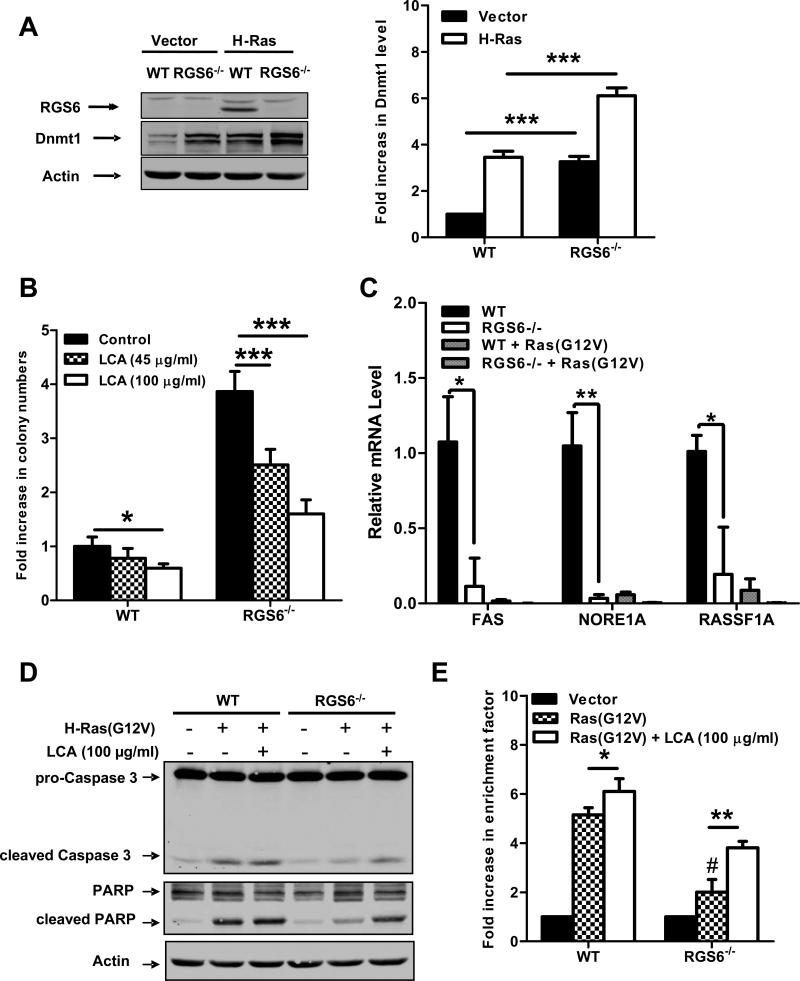
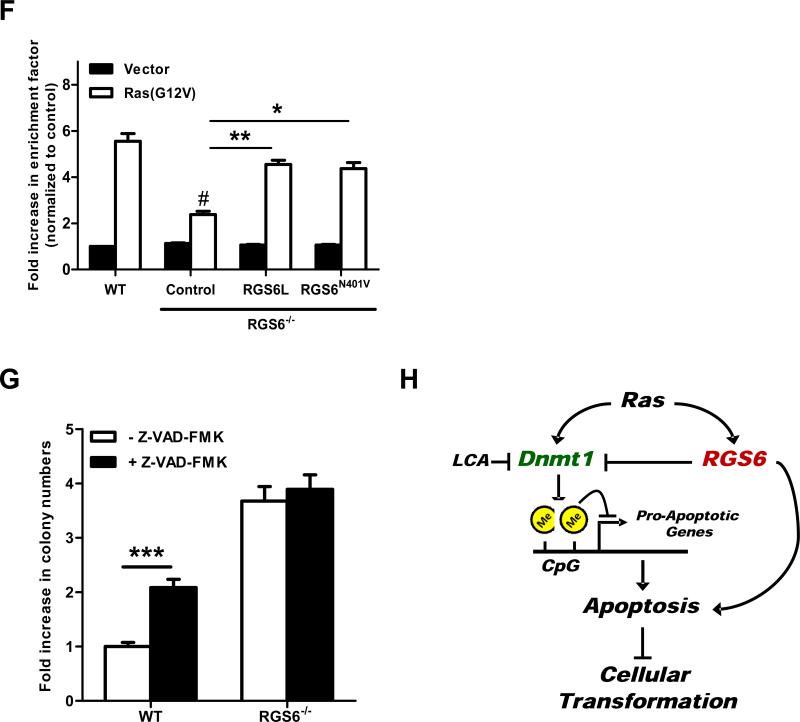
Fig. 2.
RGS6 is induced by Ras and blocks Ras-induced transformation by down-regulating Dnmt1 and suppressing Dnmt1-mediated apoptosis. (A) Representative immunoblots (left panel) of RGS6 and Dnmt1 and summary data (right panel) of Dnmt1 levels in MEFs expressing control vectors or H-Ras(G12V) /p53(R175H). Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of genotype (F1,8 = 354.05; p<0.0001) and H-Ras infection (F3,40 = 304.21; p<0.0001) on Dnmt1 expression. H-Ras expressing MEFs were prepared as described in Fig 1. MEFs were grown in normal culture medium for 2 weeks after antibiotics selection. Cell lysates were then prepared and subjected to immunoblotting as previously described(7). Antibodies used were: RGS6 (prepared in the lab(7), 1:5000); Dnmt1 (Santa Cruz, 1:1000); Actin (Sigma, 1:2000). (B) LCA blocks enhancement of Ras-induced colony formation by RGS6−/− MEFs. There was a significant effect of genotype (F1,40 = 521.02; p<0.0001) and drug treatment (F2,40 = 89.92; p<0.0001). Ras-induced colony formation in soft agar by WT or RGS6−/− MEFs was performed in the presence and absence of the indicated concentrations of LCA as described in Fig. 1. (C) Loss of RGS6 promotes silencing of pro-apoptotic Dnmt1 target genes FAS, NORE1A, and RASSF1A. For each gene there was a significant effect (p<0.05) of genotype and transfection condition by two-way ANOVA. H-Ras(G12V) was transiently transfected into MEFs using Lipofectamine 2000 as described(7). mRNA from control and Ras(G12V) transfected MEFs was prepared using a Qiagen RNeasy Mini kit and first stand cDNA synthesis was performed with SuperScript III (Invitrogen, CA). Real time PCR was carried out using iQ™ SYBR® Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, CA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. PCR primers used are outlined in Table S1 and 18s rRNA was used as an internal control to normalize RNA levels. Ras-induced caspase 3 and PARP cleavage (D) and apoptosis (E) is impaired in RGS6−/− MEFs and partly restored by treatment with LCA. For apoptosis assay two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of genotype (F1,12 = 127.24; p<0.0001) and drug treatment (F2,12 = 207.68; p<0.0001). Apoptosis is expressed as a fold increase in enrichment factor (cytoplasmic nucleosomes, i.e. cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments) measured with the Roche Cell Death Detection Kit. Apoptosis was analyzed 72 hours after H-Ras(G12V) transfection. (F) RGS6L and RGS6LN401V rescue restores the impaired Ras(G12V)-induced apoptotic response (methods described in legend of Fig. 2E) in RGS6−/− MEFs. Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of RGS6 transfection condition (F3,16 = 23.13; p<0.0001). Cells were cotransfected with and without H-Ras and indicated RGS6 construct using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's protocol. (G) Inhibition of apoptosis enhances HRas(G12V)/ p53(R175H)-induced colony formation in WT but not RGS6−/− MEFs (n = 9). Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of genotype (F1,32 = 1047.69; p<0.0001) and drug treatment (F1,32 = 87.83; p<0.0001). Soft agar colony assays in WT and RGS6−/− MEFs were performed in the presence and absence of pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (40 μM, Sigma) as described in Fig. 1. (G) Schematic diagram illustrating the role of RGS6 in Ras-induced oncogenic transformation. Oncogenic Ras induces RGS6 which directly induces apoptosis and suppresses Dnmt1 protein expression, thereby impairing Dnmt1 silencing of apoptotic genes. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; #, p<0.001 vs. WT + H-Ras (bonferroni multiple comparisons). Unless otherwise indicated all experiments were performed in triplicate. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M.