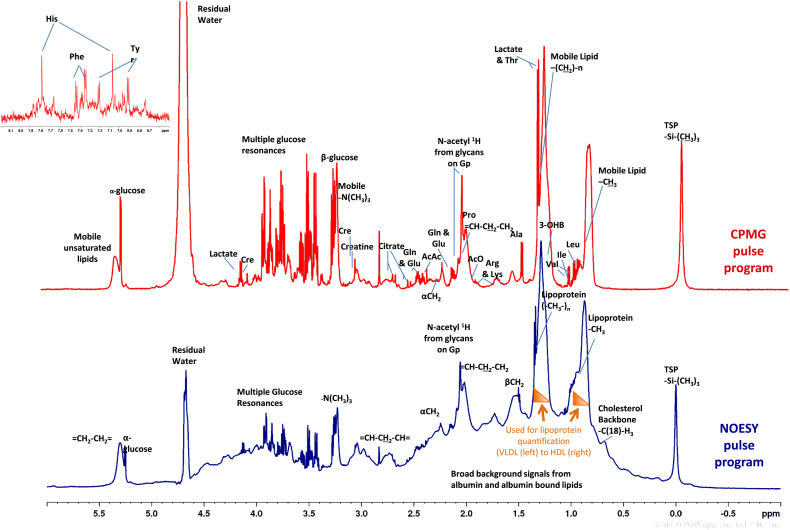
Fig. 2.
Typical 1H NMR spectra of serum analysed with two different pulse programs. Nuclear Overhauser Effect Spectroscopy (NOESY in blue) experiment used for Lipoprotein quantification and Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill (CPMG in red) experiment used to quantify low molecular weight metabolites. Insert shows the aromatic region of the CPMG spectrum. Spectra were analysed and interpreted using the Finnish method (35, 42). The broad resonances arising from methy and methylene groups of lipoprotein lipids depend on the composition and size of the lipoprotein and can be deconvoluted to quantify lipoprotein subfractions. Key: TSP; 3-(trimethylsilyl)-2,2’,3,3’-tetradeuteropropionic acid; N-acetyl 1H from glycans on Gp; glycoprotein (mostly α-1-acid glycoprotein); Leu: leucine; Ile: isoleucine; Val: valine; Thr: threonine; 3-OHB: 3-hydroxybutyrate; Ala; alanine; Arg: arginine; Lys: lysine; AcO; acetate; Pro: proline; Gln: glutamine: Glu: glutamate; AcAc: acetoacetate; Cre: creatinine; His: histidine; Phe: phenylalanine; Tyr: tyrosine. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)