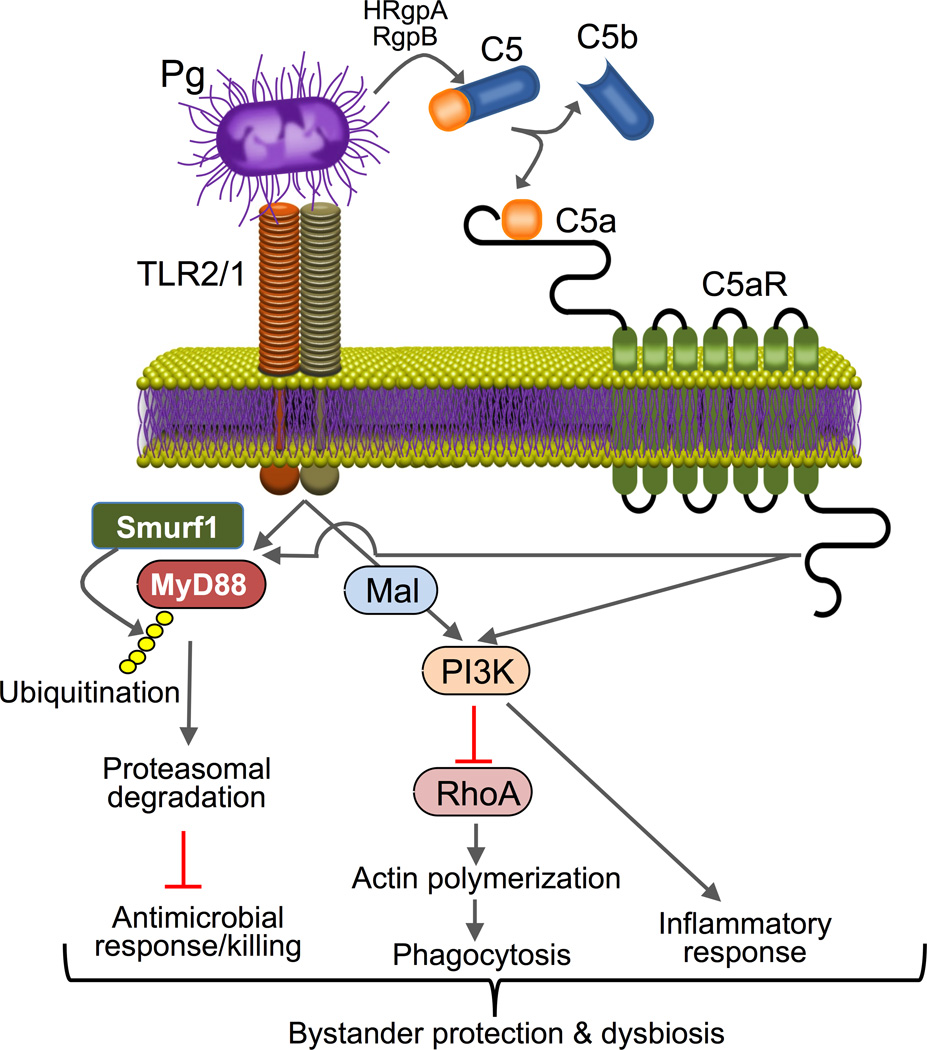
Figure 2. Model of P. gingivalis subversion of neutrophils leading to dysbiotic inflammation.
P. gingivalis co-activates TLR2 and C5aR in neutrophils and the resulting crosstalk leads to E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1-dependent ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of MyD88, thereby inhibiting a host-protective antimicrobial response. Moreover, the C5aR-TLR2 crosstalk activates PI3K, which prevents phagocytosis through inhibition of RhoA activation and actin polymerization, while stimulating an inflammatory response. In contrast to MyD88, Mal is a component of the subversive pathway acting upstream of PI3K. The integrated mechanism provides ‘bystander’ protection to otherwise susceptible bacterial species and promotes polymicrobial dysbiotic inflammation in vivo. From Maekawa et al., 2014b with permission.