Fig. 4.
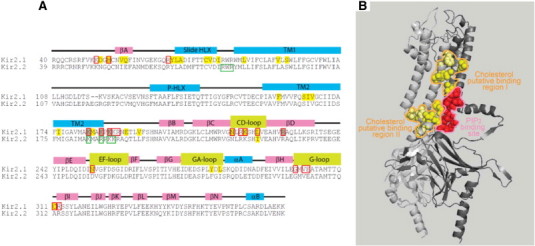
A: Overlap between residues involved in cholesterol or PIP2 sensitivity of Kir2.1. The figure shows sequence alignment of the Kir2.1 and Kir2.2 channels with key secondary structural elements labeled above the sequence. Residues that were found to affect the cholesterol sensitivity of the channel in functional studies are highlighted yellow. Red boxes highlight residues that were found to play an important role in channel-PIP2 interactions in functional studies. Yellow-filled red boxes highlight residues whose mutation affects both channel–PIP2 interactions and the sensitivity of the channel to cholesterol. Light brown-filled red boxes filled in light brown highlight residues whose mutation to glutamine affects channel–PIP2 interactions but does not affect the sensitivity of the channel to cholesterol. Green boxes highlight residues with direct bonding interactions to PIP2 as determined using crystallography. B: A lack of overlap between the PIP2-binding site and putative cholesterol-binding sites in Kir2.2. A ribbon presentation of two adjacent subunits (Gray and light gray) of the crystal structure of Kir2.2 (PDB ID 3spi) showing the binding site of PIP2 in the channel (red balls). Also shown are the corresponding Kir2.2 residues to Kir2.1 residues that form two putative cholesterol binding sites in Kir2.1 based on functional data and molecular modeling (yellow balls — direct interaction; light yellow balls — secondary effect within 4 Å from directly interacting residues).
