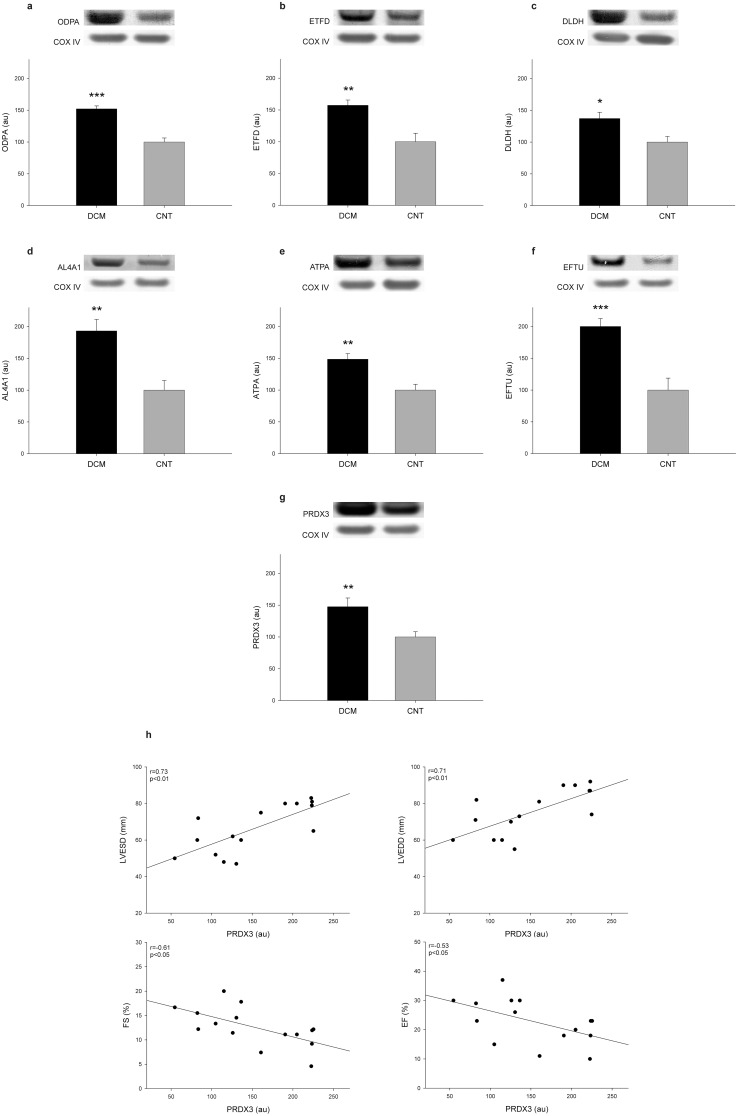
Figure 1. Mitochondrial protein overexpression in dilated human hearts and relationship between PRDX3 and left ventricular function.
(a–g) The influence of dilated cardiomyopathy on the amount of each representative protein involved in cardiac energy metabolism (ODPA, ETFD, DLDH, AL4A1, and ATPA), protein biosynthesis (EFTU), and stress response (PRDX3) analyzed using western blotting techniques. As shown, all proteins were significantly increased in the DCM group (n = 17) compared with the CNT group (n = 8). The values from the controls were set to 100. Values were normalized to COX IV and finally to the CNT group. The data are expressed as mean+SEM in arbitrary units (optical density). Images are representative of the results obtained for all of the patients with DCM and the CNT included in the study. (h) Scatter plots showing the relationship between PRDX3 protein levels and left ventricular function, specifically with fractional shortening, left ventricular end systolic diameter, and left ventricular end diastolic diameter. CNT, control; DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy; ODPA, pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit α, somatic form; ETFD, electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase; DLDH, dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase; AL4A1, delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase; ATPA, ATP synthase subunit α; EFTU, elongation factor Tu; PRDX3, thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase; FA, fractional shortening; LVESD, left ventricular end systolic diameter; LVEDD, left ventricular end diastolic diameter. *p value<0.05, **p value<0.01, ***p value<0.0001.