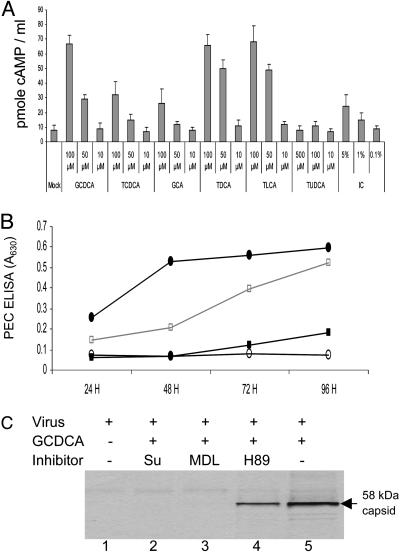
Fig. 4.
Effects of bile acids or IC on induction of cAMP in LLC-PK cells and of various PKA signaling pathway inhibitors on bile acid-mediated PEC growth. (A) cAMP induction by various concentrations of conjugated bile acids in LLC-PK cells. Confluent 3- to 4-day-old LLC-PK cell monolayers were incubated with various concentrations of GCDCA, TCDCA, GCA, TDCA, TLCA, TUDCA, or IC as indicated for 20 min in the presence of 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase. Cells were lysed, and the concentration of cAMP was measured. (B) The effects of G protein (suramin), adenylate cyclase (MDL12,330A), and PKA (H89) inhibitors on PEC growth in the presence of GCDCA was examined. After virus inoculation of 3- to 4-day-old LLC-PK cells, cells were incubated with 100 μM of GCDCA alone (•) or 100 μM of GCDCA in the presence of 200 μM of suramin (○), 20 μM of MDL12,330A (▪), or 20 μM of H89 (□). PEC antigen was assayed by ELISA. (C) PEC-infected cells were incubated with medium only (lane 1), 100 μM of GCDCA alone (lane 5), or 100 μM GCDCA with suramin (200 μM, lane 2), MDL12,330A (20 μM, lane 3), or H89 (20 μM, lane 4). PEC-infected cells were 35S-Met- and 35S-Cys-labeled at 48 h after virus infection for 4 h, and cell lysates were analyzed by RIPA with αPEC VLP serum.