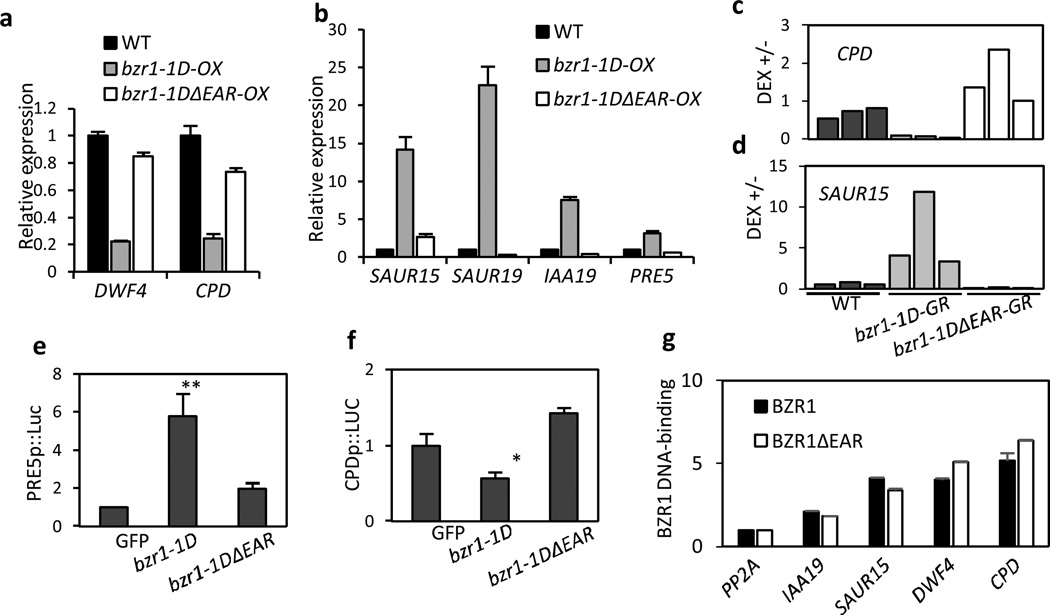
Fig. 2. EAR motif mediates BZR1 regulation of gene expression.
(a,b) The deletion of EAR motif abolishes BZR1 regulation of gene expression. Seedlings were grown on the medium containing 2 µM PPZ in the dark for 5 days before harvesting for RNA extraction. Gene expression levels are normalized to that of PP2A and are shown relative to the expression levels in wild type (Col-0).
(c,d) The EAR motif-deleted bzr1-1D neither represses CPD expression (c) nor activates SAUR15 expression (d). Four-week-old leaves of transgenic plants expressing bzr1-1D-GR or bzr1-1DΔEAR-GR were treated with mock or 40 µM of dexamethasone (DEX) for 4 hr. Ratios of expression levels in DEX-treated to mock-treated are shown. Each bar represents independent transgenic plant.
(e,f) The EAR motif-deleted bzr1-1D cannot activate PRE5 promoter activity (e) and cannot repress CPD promoter activity (f) in a transient gene expression assay. The 2 kb of PRE5 promoter or 1 kb of CPD promoter fused to fire fly luciferase reporter gene was co-transfected with 35S::bzr1-1D or 35S::bzr1-1DΔEAR into Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplast. The fire fly luciferase activities were normalized by renilla luciferase as an internal control and are shown relative to that of protoplasts transfected with 35S::GFP (GFP). ** : P<0.01 and * : P<0.05 by Student’s t-test.
(g) The deletion of EAR motif does not affect BZR1 DNA-binding. Transgenic plants overexpressing BZR1 and BZR1ΔEAR were treated with 100 nM BL and crosslinked for the ChIP assays. In the ChIP assays, the enrichment of DNA was calculated as the ratio between transgenic plants and wild type control (Col-0), normalized to that of the PP2A coding region as an internal control.
Error bars in (a,b,e,f,g) indicate the s.d. (n=3).