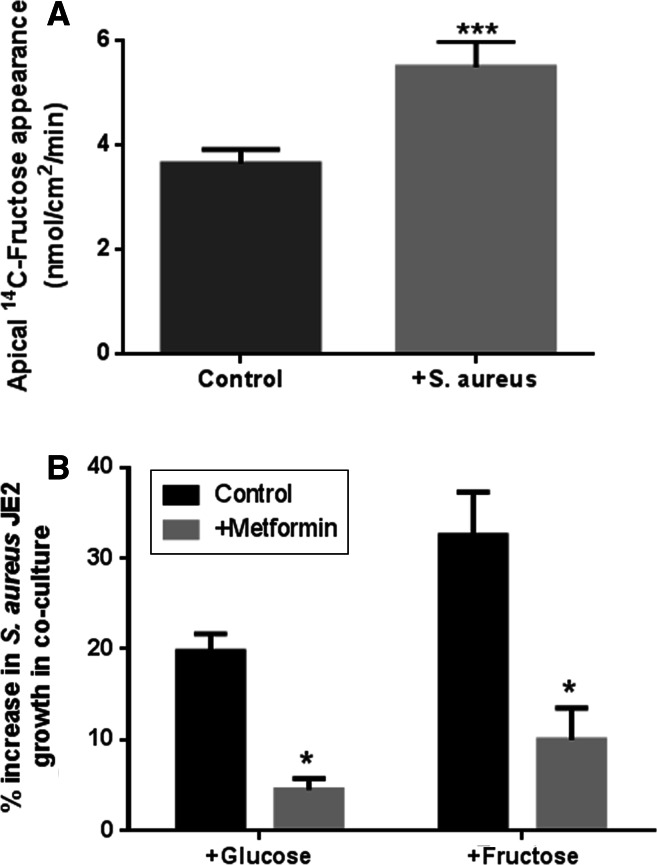
Fig. 5.
Metformin reduced the transepithelial flux of fructose and inhibited fructose-induced S. aureus JE2 growth across airway epithelial monolayers. a The effect of metformin pre-treatment of H441 airway epithelial monolayers (1 mM; 18 h pre-treatment) on the fructose-induced growth of apical S. aureus JE2. H441 airway epithelia-bacteria co-cultures were grown in basolateral Krebs salt solution supplemented with 5 mM glucose (control) or 5 mM glucose + 15 mM fructose (fructose-induced growth). S. aureus CFU were measured 7 h post infection (% increase compared to growth in the presence of 5 mM basolateral glucose), n = 4. b Transepithelial flux of fructose across untreated and metformin pre-treated H441 monolayers, measured by adding radiolabelled d-fructose to the basolateral surface and monitoring its appearance of the apical surface, n = 4. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, compared to control