Fig. 4. AKT1 knockdown induces Cytoophida formation.
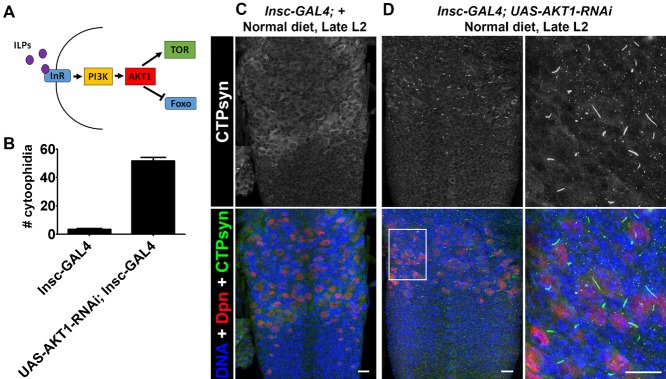
(A) When nutrients are available insulin-like peptides (ILPs) bind the insulin receptor (InR), activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. This in turn inhibits the growth inhibitor Foxo and activates TOR, leading to growth and division of cells, including neuroblasts. (B) AKT1 was knocked down in neuroblasts using Insc-GAL4, UAS-AKT1-RNAi to mimic nutritional stress. AKT1 knockdown induces cytophidia formation. (C) Insc-GAL4 controls displayed very few neuroblasts with cytophidia. (D) Cytophidia in Insc-GAL4, UAS-AKT1-RNAi neuroblasts. These images are representative of >6 animals imaged. Scale bars: 10 µm.
