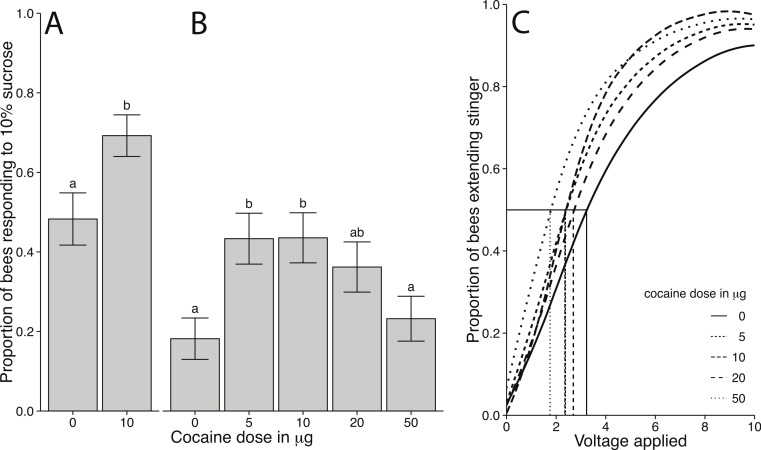
Figure 3. Behavioural responsiveness following cocaine administration in honey bees.
(A) Proportion of bees responding to 10% sucrose following treatment with 0 or 10 µg of volatilised cocaine (error bars represents standard error and letters denote statistically different groups). There was a significant increase in sucrose responsiveness in bees treated with 10 µg cocaine relative to control (χ2 = 6.1013, df = 1, p = 0.0135). (B) Proportion of bees responding to 10% sucrose following treatment with 0, 5, 10, 20, or 50 µg of volatilised cocaine. There was a dose-dependent relationship between cocaine dose and sucrose responsiveness (χ2 = 14.089, df = 4, p = 0.0070). (C) Shock responsiveness of bees following cocaine administration. Curves are based on weibull distributions of shock responsiveness for each group. Comparisons are based on estimates of EV50 for 40 bees per group (F4,40 = 5.4, p = 0.0015). Pairwise comparisons found that the 50 µg group was different from all other groups, while the remaining cocaine treated groups were different from controls.