Fig 7.
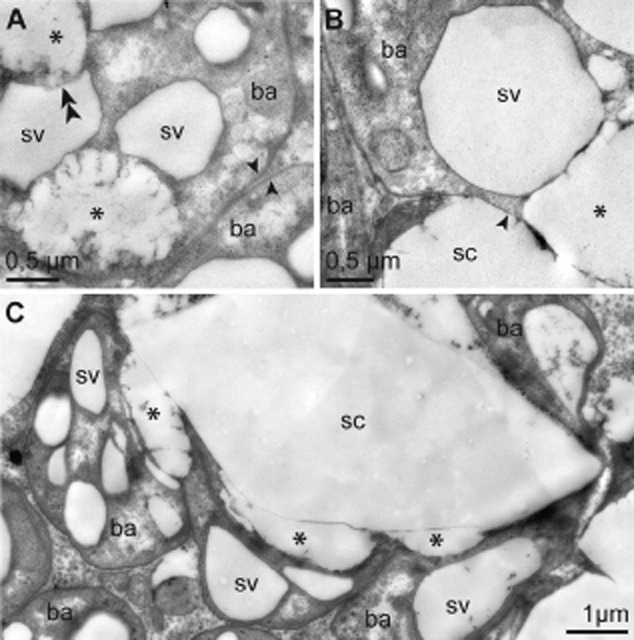
Sulfur crystal formation by the symbionts (TEM). A. Symbionts with intact cell wall (arrow), sulfur vesicles and remnants of sulfur vesicles caused by disintegration of vesicle membranes, indicated by double arrowhead. B. Detail of symbiont with partially disintegrated cell wall. Transition between intact and disintegrated cell wall is indicated by arrowhead. Remnant of sulfur vesicle next to sulfur crystal located within the bacteriocyte cytoplasm. C. Sulfur crystal completely surrounded by symbionts. Remnants of sulfur vesicles are located next to a crystal. Bacterial areas adjacent to a crystal lack a cell wall. Asterisk indicates remnant of bacterial sulfur vesicle. Note that neither the content of sulfur vesicles nor the crystals are actually still present in the TEM micrographs because of dissolution of sulfur during the dehydration and embedding process. Ba, bacterium; sc, sulfur crystal; sv, sulfur vesicle.
