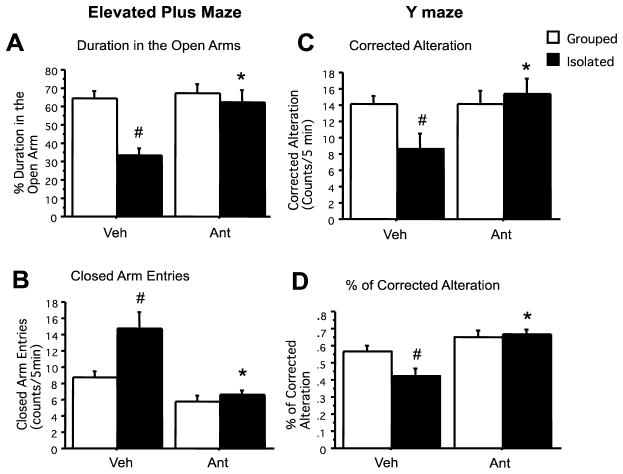
Figure 4. Antalarmin blocks stress–induced increases in anxiety and memory-related behavior related behavior in Tg2576 mice.
Chronic isolation stress significantly decreases the amount of time in the open field arm (A: #P<.01) and increases the number of entries in the closed arm compared to group-housed mice (B: #P<.05). Antalarmin administration ameliorated isolation stress–induced anxious behavior by increasing the duration in the open arm and decreasing the number of entries in the closed arm compared to isolated vehicle-treated mice (A, B: *P<.01). After chronic isolation stress, Tg2576 mice demonstrated less alternation and decreased rate of correct alternation as compared to group-housed mice (C, D: #P<.05). Again, antalarmin administration significantly restored number (C) and percentage (D) of correct alternation behaviors as compared to the isolated vehicle group (C, D: *P<.01). There was no difference in the total arm entries between isolated and group-housed animals.