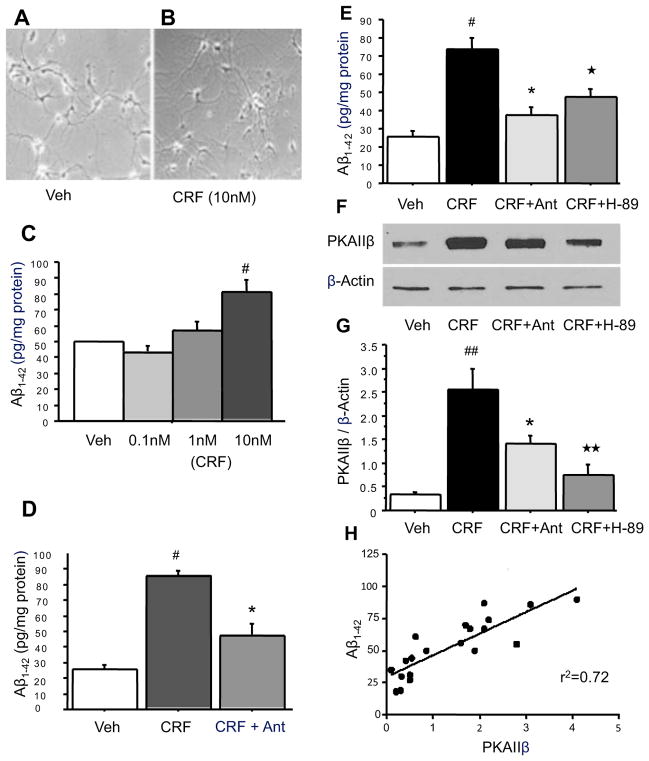
Figure 5. Antalarmin inhibits the effect of CRF on Aβ1-42 levels through the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway.
Primary hippocampal neurons derived from Tg2576 mice cultured at 16 days without CRF (A) and with CRF for 48 hours (B). ELISA analysis indicates that 10nM but not 0.01nM or 1nM CRF administered to medium of primary neurons at 14 days significantly increased Aβ1-42 levels after 48 hours of CRF exposure as compared to vehicle control (C: #P<.05). Treatment with 10nM CRF plus 100nM antalarmin blocked the increases of Aβ1-42 levels compared to CRF treated groups (D: #P<.001: CRF vs. Veh; *P<.01: CRF vs CRF+Ant). H-89, a PKA inhibitor, co-treated with CRF blocked CRF effect on Aβ1-42 levels (E: ★P<.05: CRF vs CRF+H-89). Western blotting analysis indicates that CRF significantly increased PKAIIβ expression, and antalarmin can block this effect. Treatment of PKA inhibitor H-89 also blocked CRF induced increase of PKAIIβ expression (F, G: #P<.001: CRF vs. Veh; *P<.05: CRF vs CRF+Ant; ★★P<.01: CRF vs CRF+H-89). Linear regression analysis indicates that Aβ1-42 levels are highly correlated with PKAIIβ expression (J: r2 = 0.72, P<.0001).