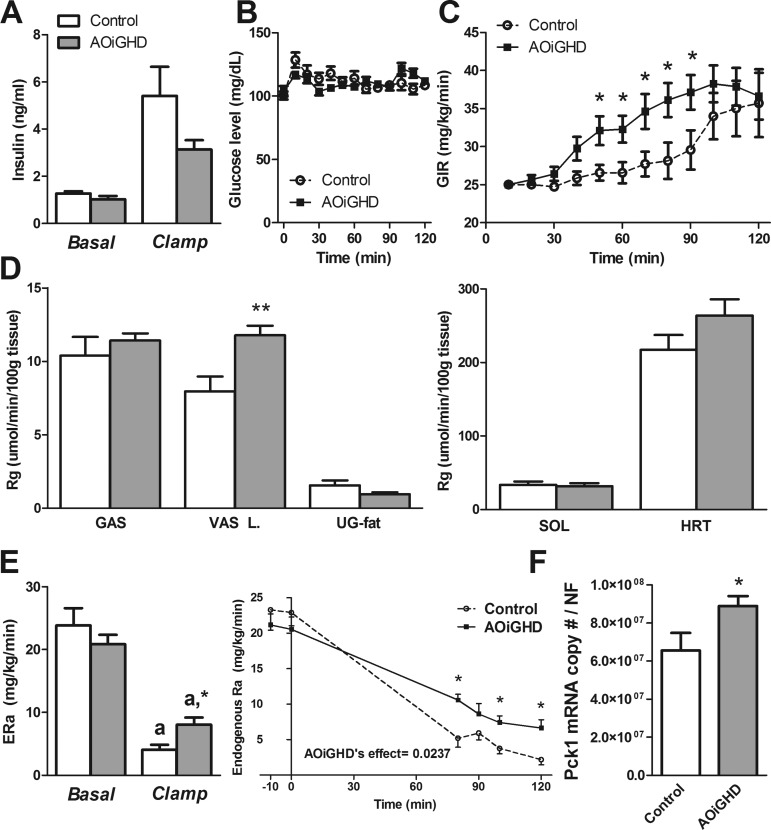
Fig. 1.
Assessment of tissue-specific insulin actions by hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps in adult-onset, isolated growth hormone deficiency (AOiGHD) and control mice, maintained on a low-fat (LF) diet. A: plasma insulin levels before and after hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. B and C: blood glucose (B) and glucose infusion ratio (GIR, C) during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. D: tissue-specific glucose metabolic index (Rg) of gastrocnemious (GAS), vastus lateralis (VAS L), urogenital fat (UG-fat), soleus (SOL), and heart (HRT). E: endogenous glucose production (ERa) before and after hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp [n = 8–9 mice/group, 30–32 wk of growth hormone deficiency (GHD), LF feeding started at 4 wk of age]. F: hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (Pck1) expression of AOiGHD and control mice (28 wk of GHD, chow fed, n = 5–14 mice/group). aSignificant difference between clamped and basal state within genotype (E). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, significant difference between control and AOiGHD mice (C, D, E, and F).