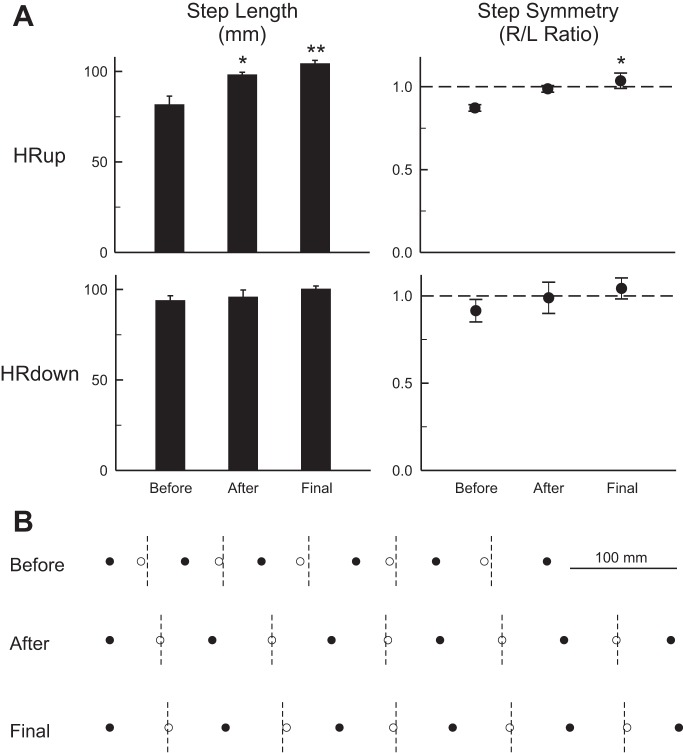
Fig. 4.
A: impact of H-reflex conditioning on step cycle length and step symmetry. A: average step-cycle length (left) and right/left step cycle symmetry (right) (±SE) before and immediately after up- or down-conditioning and at the end of data collection. Up-conditioning produced persistent improvements in step cycle length and right/left step cycle symmetry (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. before; Tukey test). Down-conditioning had no significant effect on step cycle length or on right/left symmetry. B: data from a representative HRup rat illustrating the persistent impact of up-conditioning on step cycle length and symmetry. ● and ○, Onsets of right and left stance, respectively. Dashed vertical lines are halfway between right stance onsets, when left stance onset should occur. Prior to conditioning, right stance is not adequately maintained and left stance onset occurs too early (i.e., the rat limps). After up-conditioning, the steps are longer and left stance onset occurs on time. These improvements persist 100 days later.