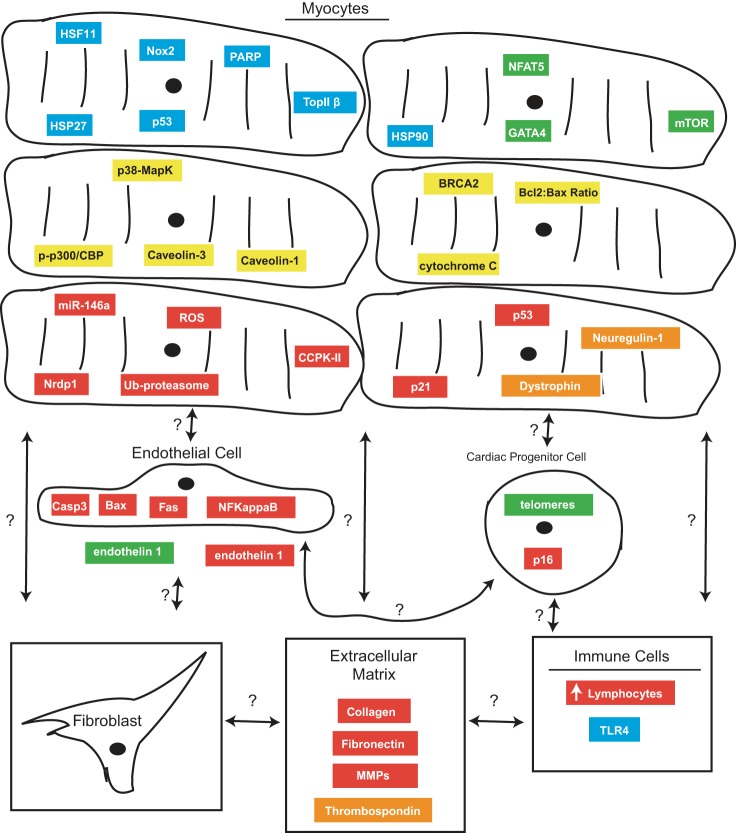
Fig. 2.
Summary of myocardial cellular effects and the injury response induced by anthracyclines. Blue, absence abrogates cardiac dysfunction or protects from apoptosis; green, downregulation of mRNA and pathway inhibition; yellow, mediates apoptotic response; red, expression increases or enhances cardiac dysfunction; orange, absence enhances cardiac dysfunction. Anthracycline exposure increases p53, and global knockout abrogates the cardiotoxic response. HSF11, heat shock factor 11; Nox2, cofactor for NADPH oxidase; TopIIβ, topoisomerase II-β; HSP27, heat shock protein 27; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase; HSP90, heat shock protein 90; GATA4, transcription factor; NFAT5, nuclear factor of activated T cells; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; p38-MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; p-p300/CBP, phosphorylated p300/CREB binding protein; BRCA2, breast cancer susceptibility gene 2; Bcl2:Bax ratio, ratio of B-cell lymphoma 2 to bcl2-like protein 4; miR-146a, microRNA 146a; ROS, reactive oxygen species; CCPK-II, calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; Nrdp1, E3 ubiquitin ligase; Ub-proteasome, ubiquitinated proteasome; Casp3, caspase 3; Bax, bl2-like protein 4; Fas, ligand for Fas receptor; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κ light chain enhancer of activated B cells; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4.