Figure 12.
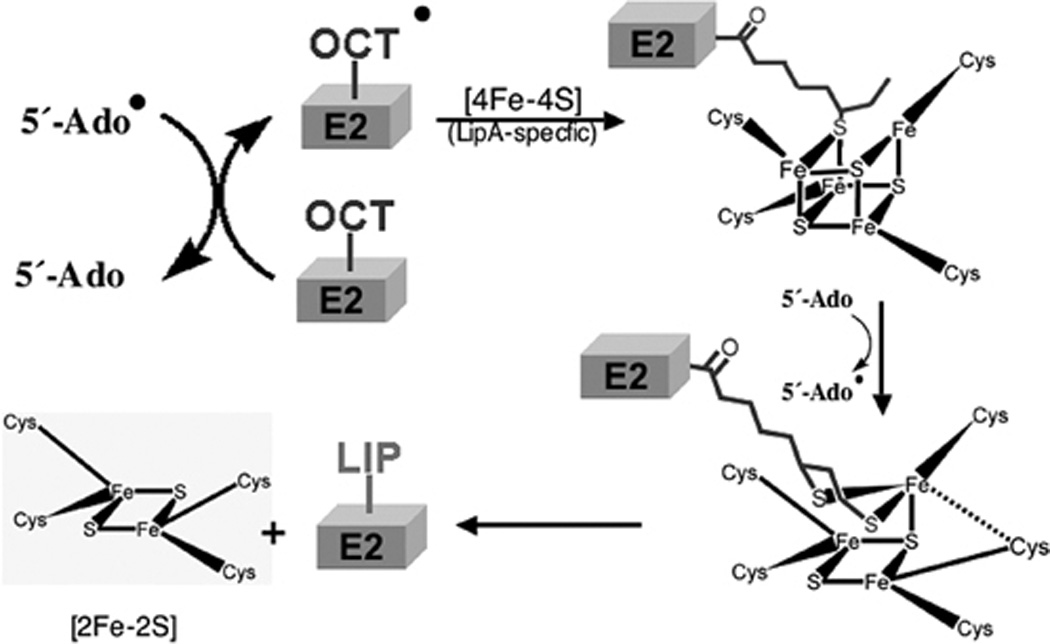
A current model of the lipoate synthase (LipA) reaction (202, 203, 240). The canonical SAM radical [4Fe-4S] cluster of LipA reduces SAM to generate the deoxyadenosine radical (5′-Ado) as seen previously in the BioB reaction (Fig. 4). The radical then removes a hydrogen atom from the C6 methylene of the octanoate moiety of an octanoyl domain (Oct-E2 on the Figure) (229) to give a carbon radical that then attacks the lipoyl synthase-specific [4Fe-4S] cluster and abstracts a reduced sulfur atom. This process is repeated at the methyl carbon (C8) to give lipoyl-domain (Lip-E2, probably as the dihydrolipoyl form due to the strongly reducing conditions under which the reaction proceeds).
