Fig. 6.
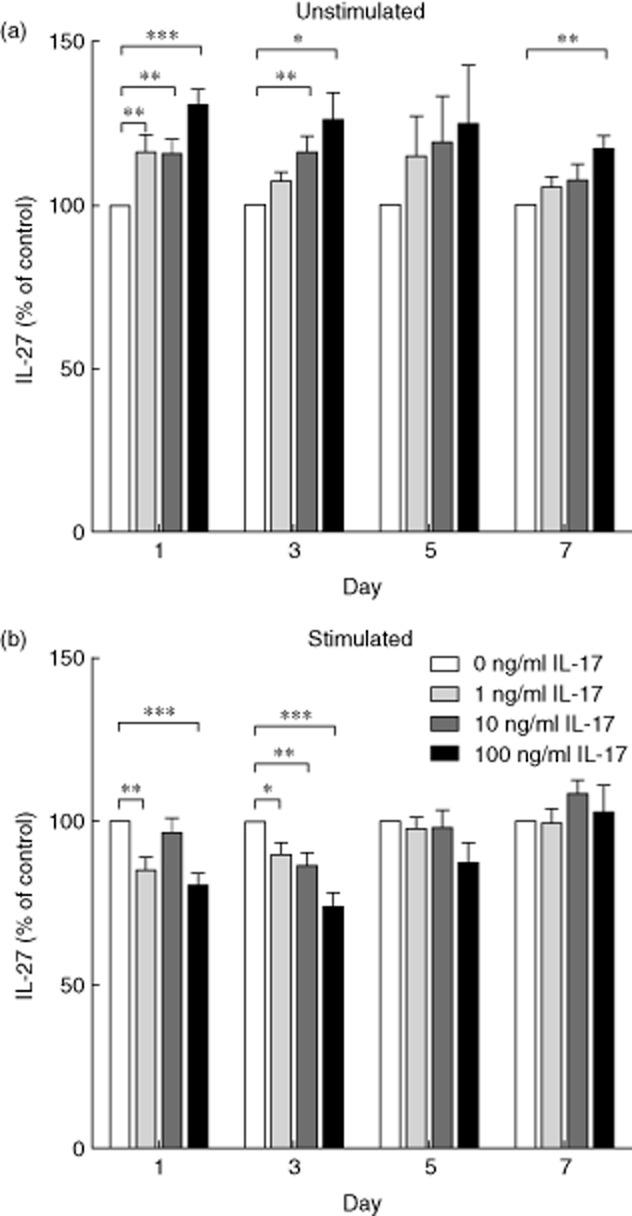
Interleukin (IL)-27 concentrations in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) cultures in response to the addition of recombinant human interleukin (rhIL)-17A. PBMC were isolated from healthy donors and cultured in the presence of varying concentrations of rhIL-17A (0, 1, 10 or 100 ng/ml). On days 1, 3, 5 and 7 the concentration of IL-27 in the supernatant was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (a) PBMC were left unstimulated, significant differences were observed on days 1, 3 and 7. Day 1, 0 versus 1 ng/ml P = 0·003; 0 versus 10 ng/ml P = 0·005; 0 versus 100 ng/ml P < 0·001. Day 3, 0 versus 10 ng/ml P = 0·005; 0 versus 100 ng/ml P = 0·012. Day 7, 0 versus 100 ng/ml P = 0·003. n = 15. (b) T cells within the PBMC were stimulated by plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28. Significant differences were observed on days 1 and 3. Day 1, 0 versus 1 ng/ml P = 0·003; 0 versus 100 ng/ml P,0·001. Day 3, 0 versus 1 ng/ml P = 0·027; 0 versus 10 ng/ml P = 0·006; 0 versus 100 ng/ml P < 0·001. n = 15. The graph demonstrates percentage level compared to 0 ng/ml ± standard error of the mean. Wilcoxon's signed-rank test, *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01, ***P < 0·001.
