Figure 4.
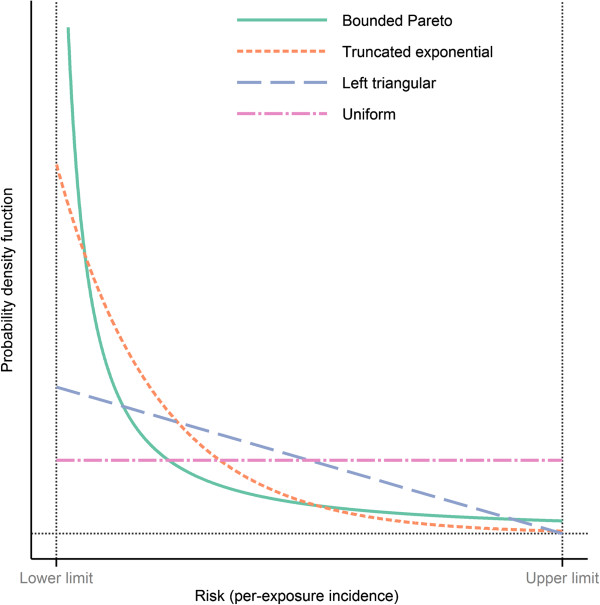
Examples of probability distributions to use over risk intervals in probabilistic analyses. In this example the lower limit is 0.03% and the upper limit 1%. The bounded Pareto distribution has a scale parameter of 0.25 and the exponential distribution has a rate parameter of 5/(Upper limit-Lower limit) before truncation. The uniform distribution corresponds to equal belief in all risks between the lower and upper limits. In contrast, the triangular distribution with mode at the lower limit puts more density on lower risks, but is still fairly likely to yield high values. Both the bounded Pareto and the truncated exponential clearly favour lower risks. Their main difference is that the former corresponds to stronger belief in risks close to both the lower and the upper limit. Note that to benefit the clarity of the display, the graph for the bounded Pareto distribution has been truncated. In reality it extends much higher for risks close to the lower limit.
