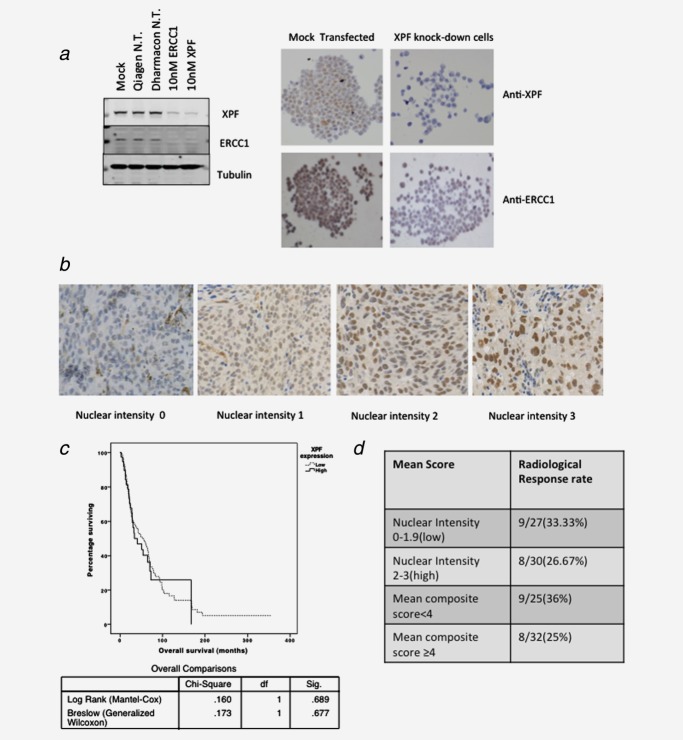
Figure 5.
Evaluation of XPF protein as a potential biomarker for sensitivity to platinum chemotherapy in paraffin-embedded human melanoma tissue. (a) Validation of anti-XPF and anti-ERCC1 antibodies for IHC on paraffin-embedded ST16 gastric carcinoma cells. Western blot showing effect of XPF and ERCC1 protein expression in ST16 cell lysates after XPF and ERCC1 knockdown using the Lipofectamine RNAiMax Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA; 13778-150), performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol using 10 nM of siRNA(Qiagen N.T. is nontargeting SiRNA). ST16 cell pellets were stained with antibodies against XPF (clone SPM228, Abcam, Cambridge, MA) with antigen retrieval in a water bath at 99°C, using 1 mM ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) buffer (pH 8.0). Primary antibody was diluted 1:100 and incubated for 2 hr at room temperature. A horseradish peroxidase based system (EnVision+; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) was used for detection of primary antibody binding. RNAi knockdown of XPF in ST16 cells produced decreased staining for XPF when compared to a mock transfection. (b) Staining for XPF on a melanoma tissue microarray, showing a variation in the levels of these proteins. (c) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the effect of XPF expression on overall survival in 183 patients with melanoma. (d) Analysis for an association between mean XPF nuclear intensity score/mean composite score and radiological response in tissue microarrays, representing cores from 57 patients with metastatic melanoma treated with cisplatin/carboplatin chemotherapy. Primary tissues were obtained from patients with MM prior to cisplatin or carboplatin chemotherapy (cutaneous = 45 patients, ocular = 3 patients, mucosal = 2 patients, unknown primary location = 7 patients). The median nuclear intensity score (2) and median composite score (4) were used to subclassify the cores into two groups. Analysis for an association between RECIST response33 and XPF score were performed using the Pearson’s chi-square test and odds ratios were calculated in SPSS version 20. Neither nuclear intensity score (α² = 0.302, p = 0.583, OR = 1.375; 95% CI = 0.441–4.291) nor composite XPF score (α² = 0.811, p = 0.368, OR = 1.688; 95% CI = 0.538–5.294) were associated with clinical response.